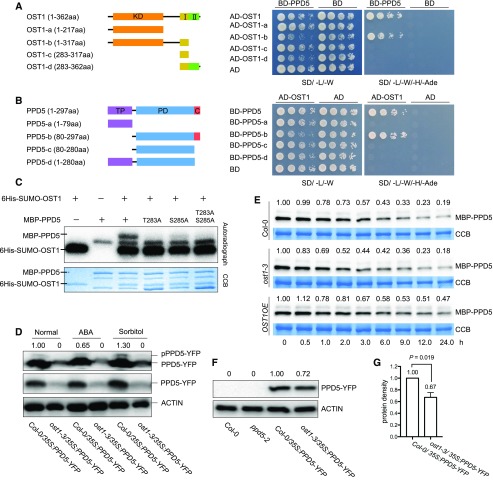
Figure 4.
OST1 phosphorylates and stabilizes PPD5. A, Yeast two-hybrid assay for the interaction between the full-length PPD5 and OST1 deletion variants. I, domain I; II, domain II. B, The interaction of OST1 and PPD5 deletion variants analyzed by yeast two-hybrid assay. PD, PsbP domain; C, C-terminal domain. C, In vitro phosphorylation assay. Recombinant proteins PPD5, PPD5T283A, PPD5S285A, PPD5T283AS285A, and OST1 were combined for the in vitro phosphorylation assay. D, In vivo phosphorylation of PPD5 by OST1 under normal, ABA, and sorbitol treatment conditions. Proteins extracted from 10-d-old seedlings after treatment were separated in a Phos-tag containing SDS-PAGE gel and immuno-detected by an anti-GFP antibody. Normal SDS-PAGE gel was used as a control. The intensity of the pPPD5-YFP bands shown above the images was quantified by using Image Lab software (version 5.2.1). E, Western blotting showing the degradation of MBP-PPD5 proteins in different genotypes using cell-free assay. Quantitation of the MBP-PPD5 band intensities was done by using the Image Lab software (version 5.2.1). F, Western blotting showing the levels of PPD5-YFP fusion proteins in transgenic plants. ACTIN was used as a loading control. The intensity of the PPD5 bands relative to the ACTIN bands was shown above the images, and the intensity was quantified by using Image Lab software (version 5.2.1). G, Statistical analysis of the result shown in (F) revealing significant differences between Col-0 and ost1-3 (n = 3). P value was determined by Student’s t test.