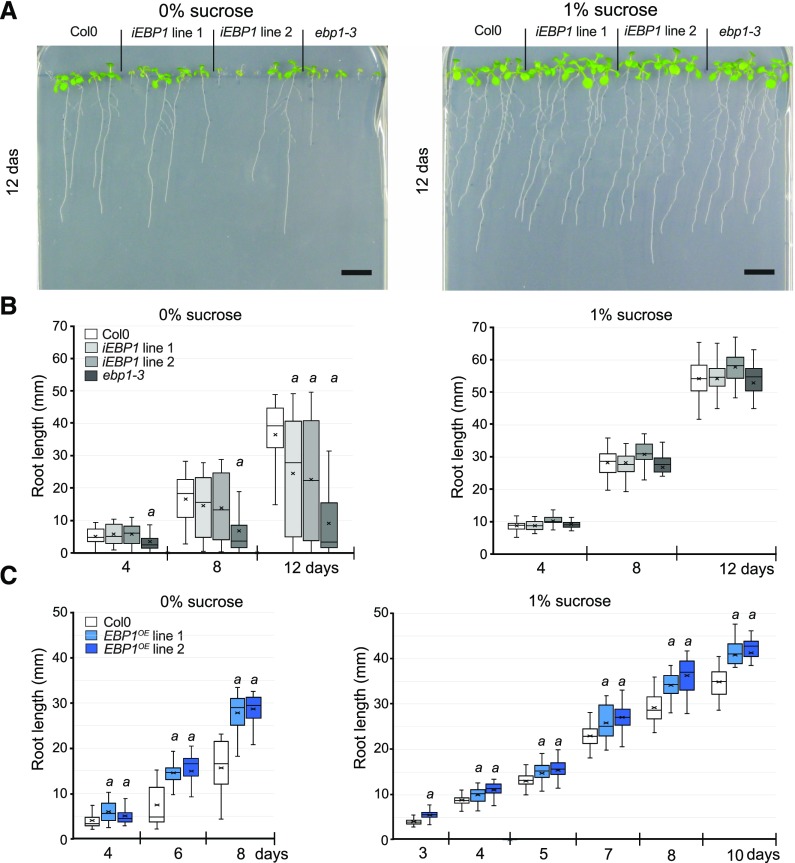
Figure 3.
Sugar can compensate for the lack of EBP1 expression and an elevated level of EBP1 can suppress sugar-dependent root growth deficiencies. A, Root growth of two independent EBP1 RNAi (iEBP1) lines and the insertional mutant, ebp1-3 compared with Col0, germinated and grown (12 d) in the absence (0%) and presence of sucrose (1%). Scale bars = 1 cm. B, Boxplot analyses show the quantification and distribution of the root length (in millimeters) of seedlings grown on 0% and 1% sucrose media at the given time points after sowing. The boxplot gives the mean line and the mean marker (cross); the quartile calculation was done exclusive of the median on root-length measurements from n = 3, n > 35 in each repeat. Significance was determined by Student t test a: P-value < 0.01. C, Quantitative analysis of root growth of the transgenic EBP1OE lines (referred as lines 19.2 and 43.2, respectively in Horváth et al., 2006) compared with Col0, germinated and grown on media with or without sucrose (0%, 1%). Boxplot analysis was carried out as in (B); n = 3, n > 35 in each repeat; significance was determined by Student t test a: P-value < 0.01. The level of EBP1 expression upon silencing and overexpression is shown in Supplemental Figure S4A and Figure 4C, respectively.