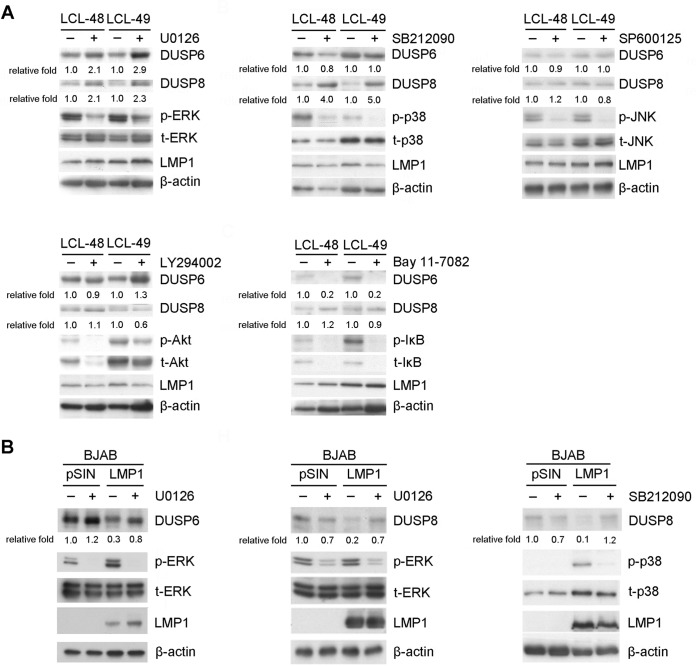
FIG 4.
Signaling pathways involved in LMP1-mediated DUSP6 and DUSP8 suppression. (A) LCLs were treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 20 μM U0126 (ERK inhibitor), 20 μM SB212090 (p38 inhibitor), 25 μM SP600125 (JNK inhibitor), 20 μM LY294002 (Akt inhibitor), or 10 μM Bay11-7082 (NF-κB inhibitor) for 2 days. Detection of DUSP6, DUSP8, phosphorylated ERK (p-ERK), phosphorylated p38 (p-p38), phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), phosphorylated IκB (p-IκB), total ERK (t-ERK), total p38 (t-p38), total JNK (t-JNK), total Akt (t-Akt), total IκB (t-IκB), and LMP1 was carried out by Western blotting. β-Actin served as an internal control. The fold relative expression data were calculated by comparing the levels of β-actin-normalized DUSP expression of the inhibitor-treated LCLs with those of the untreated LCLs. (B) BJAB cells were transduced with vector control (pSIN) or LMP1 via lentiviral infection and treated with DMSO, 20 μM U0126, or 20 μM SB212090 for 2 days. Detection of DUSP6, DUSP8, p-ERK, p-p38, t-ERK, t-p38, and LMP1 was carried out by Western blotting. The related level of expression of DUSP in vector control-transfected, untreated cells was set as a value of 1 to calculate the fold relative expression levels of DUSP6 and DUSP8.