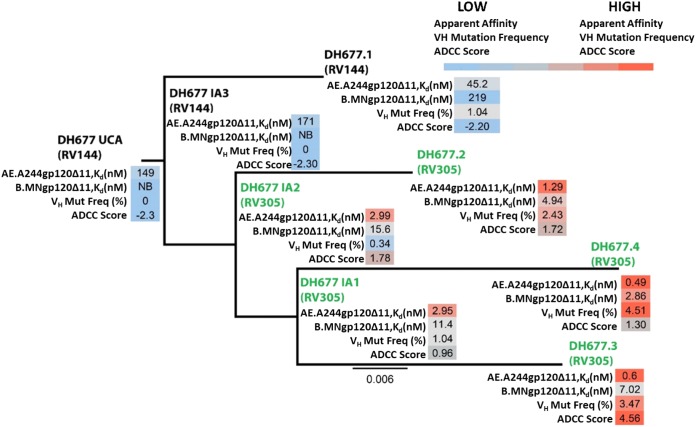
FIG 2.
RV305 boosting increased the apparent affinity and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity breadth and potency of the C1C2-specific RV144-derived DH677 memory B cell clonal lineage. DH677.1 was isolated by AE.A244gp120Δ11-specific single-cell sorting of PBMCs collected from a vaccinee 2 weeks after the final boost in the RV144 vaccine trial. DH677.2, DH677.3, and DH677.4 were isolated by AE.A244gp120Δ11-specific single-cell sorting of PBMCs collected from the same vaccinee after the second AIDSVAX B/E (RV305 group II) boost given in RV305 (∼7 years later). The intermediate ancestor one (IA1), intermediate ancestor two (IA2), intermediate ancestor three (IA3), and unmutated common ancestor (UCA) were inferred using Cloanalyst (13). The MAbs were recombinantly expressed and assayed by surface plasmon resonance for binding to the AIDSVAX B/E proteins AE.A244g120 full length, AE.A244g120Δ11, and B.MNg120Δ11. Shown are the antibody apparent affinity measurements (Kd), expressed in nanomolars. NB, no detectable binding. MAbs were also assayed for ADCC against AE.C235-, B.WITO-, C.TV-1-, C.MW965-, C.1086C-, C.DU151-, and C.DU422-infected CEM.NKRCCR5 cells. An ADCC score (see Materials and Methods) was used to account for ADCC breadth and potency.