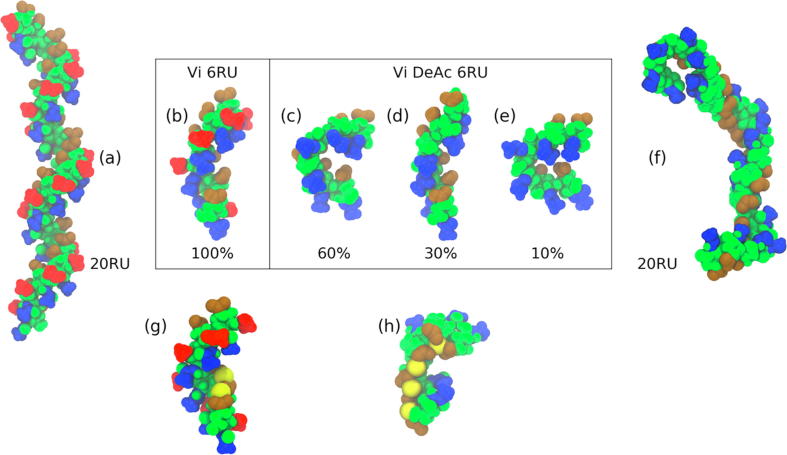
Fig. 7.
Conformations of the O-acetylated (left) and de-O-acetylated (right) Vi polysaccharide. The box shows representative structures for the dominant conformational families for the MD simulations 6RU: the acetylated strand was in a single helical conformation (b) for the entire simulation, while the de-O-acetylated strand alternated between the bent conformations shown in (c) and (d) and a helical conformation (d). The 6RU Vi PS helix can intercalate 1 to 2 sodium ions (g), whereas the more flexible de-O-acetylated strand intercalated up to 4 ions (h). The corresponding 20RU static models are shown for (a) Vi PS and (f) de-O-acetylated Vi. Atoms from the constituent groups are highlighted as follows: N-acetyl,  ; O-acetyl,
; O-acetyl,  ; carboxyl,
; carboxyl,  , with sodium ions,
, with sodium ions,  and the remaining atoms colored
and the remaining atoms colored  .
.