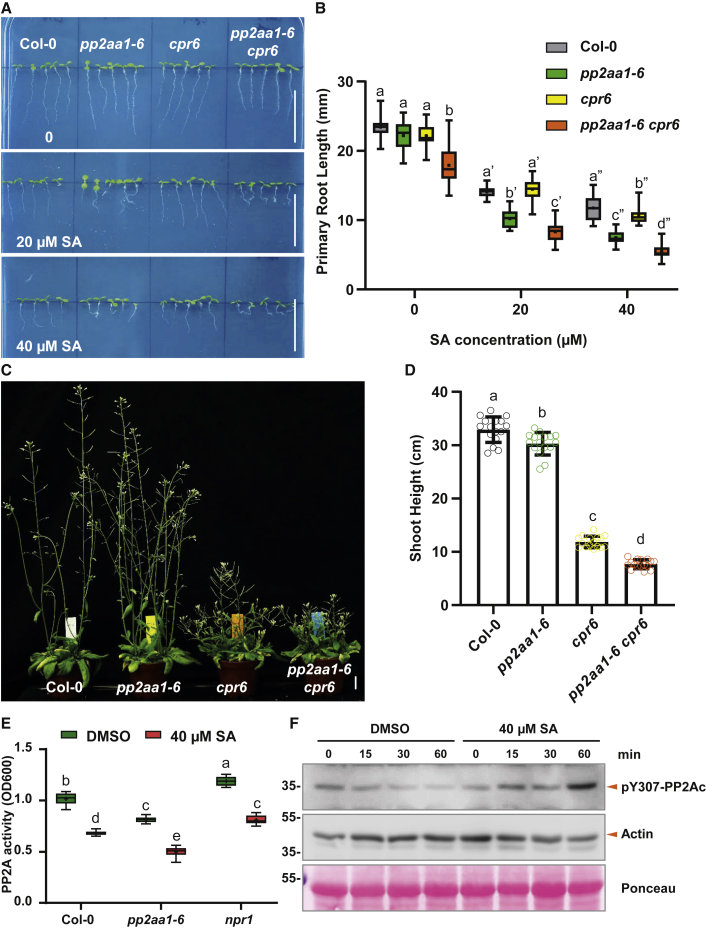
Figure 5.
Genetic Analysis of pp2aa1-6 and cpr6 Mutations, and SA Inhibits PP2A Activity In Planta
(A) Representative images showing the enhanced sensitivity of pp2aa1-6 to SA. Col-0, pp2aa1-6, cpr6, and pp2aa1-6 cpr6 seedlings were grown on plates with different concentrations of SA for 7 days. Scale bars, 2 cm.
(B) The root growth analysis revealed that the cpr6 mutation decreased the primary root length and increased the SA sensitivity of pp2aa1-6. n = 16. Different letters represent significant difference; p < 0.05; by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey multiple comparison test.
(C and D) The pp2aa1-6 mutation enhances the stunted shoot phenotype of cpr6. Col-0, pp2aa1-6, cpr6, and pp2aa1-6 cpr6 plants were grown for 38 days, and representative plants are shown (C). Scale bar, 2 cm.
(D) The height of plants was measured and shown as dot plots. Dots represent individual values, and lines indicate mean ± SD. n = 16. Different letters represent significant difference; p < 0.05; by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey multiple comparison test.
(E) SA treatment decreased the total PP2A activity in planta. Col-0, pp2aa1-6, and npr1 seedlings were grown on plates containing DMSO or 40 μM SA for 5 days and then sampled for protein isolation and PP2A activity measurement. n = 6. Different letters represent significant difference; p < 0.05; by one-way ANOVA with a Tukey multiple comparison test.
(F) SA treatment increased the phosphorylation of the PP2A catalytic subunits (PP2Ac), suggesting the decrease in PP2A activity. 7-day-old Col-0 seedlings were treated with DMSO or 40 μM SA for 0, 15 min, 30 min, and 60 min respectively, and were then collected for protein extraction and the subsequent western blot. A pY307-PP2Ac antibody was used, 1:1,000 (upper panel). The anti-actin blot (medium panel; 1:2,000) and Ponceau staining (bottom panel) indicate the loading amounts.
See also Figure S4.