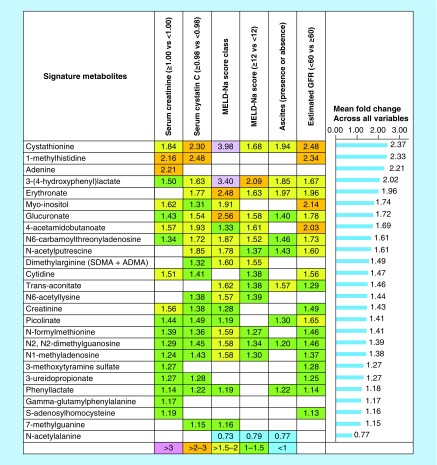
Figure 1. . Twenty-five of 33 metabolites were significantly increased and associated with at least one of the six clinical and laboratory variable categories indicative of liver and kidney disease severity in 39 patients with cirrhosis caused by primary biliary cholangitis or primary sclerosing cholangitis.
The highest mean fold-change (2.37) occurred with cystathionine when patients with low liver and kidney disease severity were compared with those with high disease severity across six clinical variables. The lowest significant positive mean fold-change (1.15) occurred with 7-methylguanine. Only one metabolite, N-acetylalanine, was significantly associated with disease severity but with a decreased mean fold-change (0.77). The corresponding cell was left blank if a metabolite did not show a significant association with the clinical and laboratory variable.
GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; MELD-Na: Model for end-stage liver disease-Na.