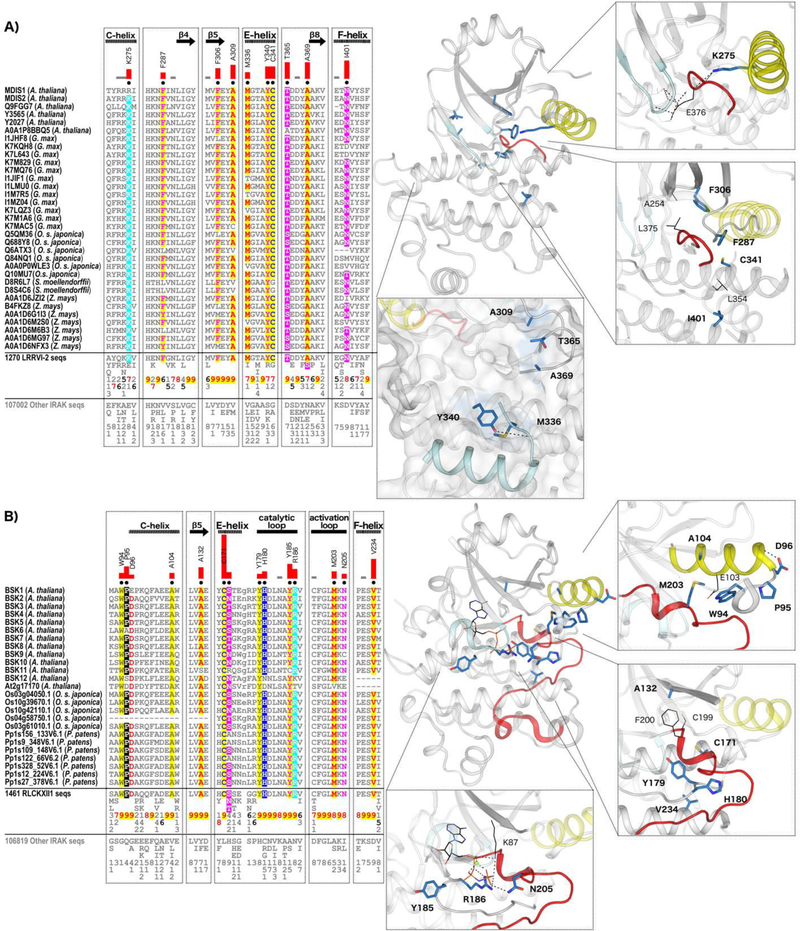
Fig. 7.
IRAK pseudokinase-specific features contribute to unique conformations in key catalytic regions. (A) LRRVI-2 pseudokinase family-specific sequence motifs. In the alignment, columns are highlighted where amino acids are highly conserved in LRRVI-2 pseudokinase family sequences and non-conserved and/or biochemically dissimilar in other IRAK sequences. Red bar lengths quantify the degree of divergence between LRRVI-2 and other IRAK sequences. Column-wise amino acid and insertion/deletion frequencies are indicated in integer tenths where a “5” indicates an occurrence of 50–60% in the given (weighted) sequence set. Columns used by the Bayesian partitioning procedure to sort LRRVI-2 sequences from other IRAK sequences are marked with black dots. Kinase secondary structures are annotated above the alignment. In the structure, the glycine-rich loop is colored in light cyan, the C-helix in yellow, and the activation loop in red. Family-specific residues are shown in blue sticks. Residues occurring in canonical catalytic motifs are shown in black lines. Hydrogen bonds are shown in dashed black lines. (B) RLCKXII-1 pseudokinase family-specific sequence motifs.