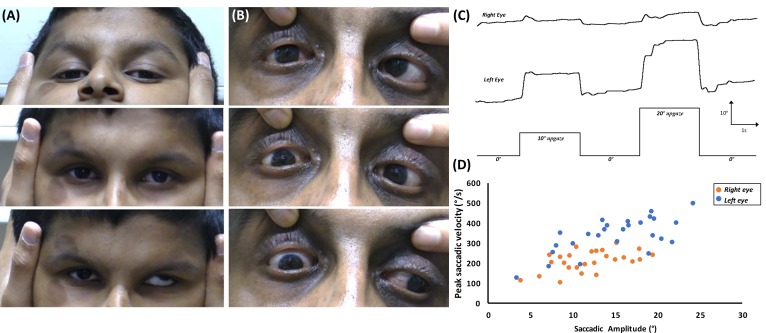
Figure 4.
(A) Rotational vestibulo-ocular reflex during pitch rotations in F1:II-1 shows lack of upward movement of the right eye. (B) Abduction of the left eye is noted on downgaze which could be a pathological synkinetic movement or due to a tight inferior rectus in F1:II-1 (upper panel=upgaze; middle panel=primary position; lower panel=downgaze). (C) Eye movement recordings in F1:II-1 showing poor elevation of the right eye from primary position. Deflection upwards represents movement of the eyes upwards, while deflection downwards represents movement of the eyes downwards. X-axis=time (in seconds); Y-axis=eye rotation (in degrees). (D) Plot of the peak saccadic velocity in relation to the saccadic amplitude, showing reduced saccadic velocity of the right eye compared with the left for upgaze.