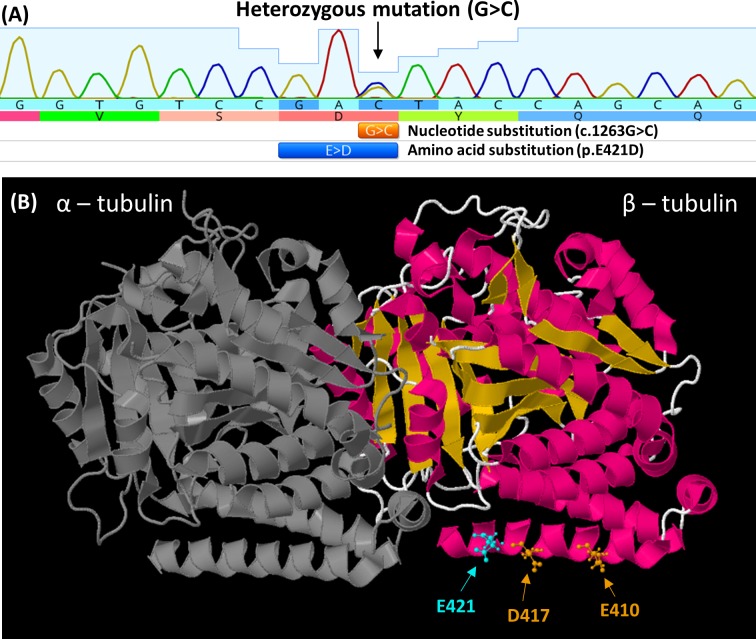
Figure 5.
(A) Electropherogram from F1:II-2, showing G>C nucleotide substitution in TUBB3. This results in the amino acid substituition glutamic acid (E) to aspartic acid (D) at amino acid position 421. (B) The location of the E421 residue (cyan) mapped on the solved protein structure of TUBB3 (PDB ID: 5IJ0). This is adjacent to previously reported mutations at residues 417 and 410 associated with congenital fibrosis of extraocular muscles (orange). All three mutations are located on the H12 α-helix and predicted to be direct binding sites required for kinesin binding to the microtubule polymer.