Figure 4.
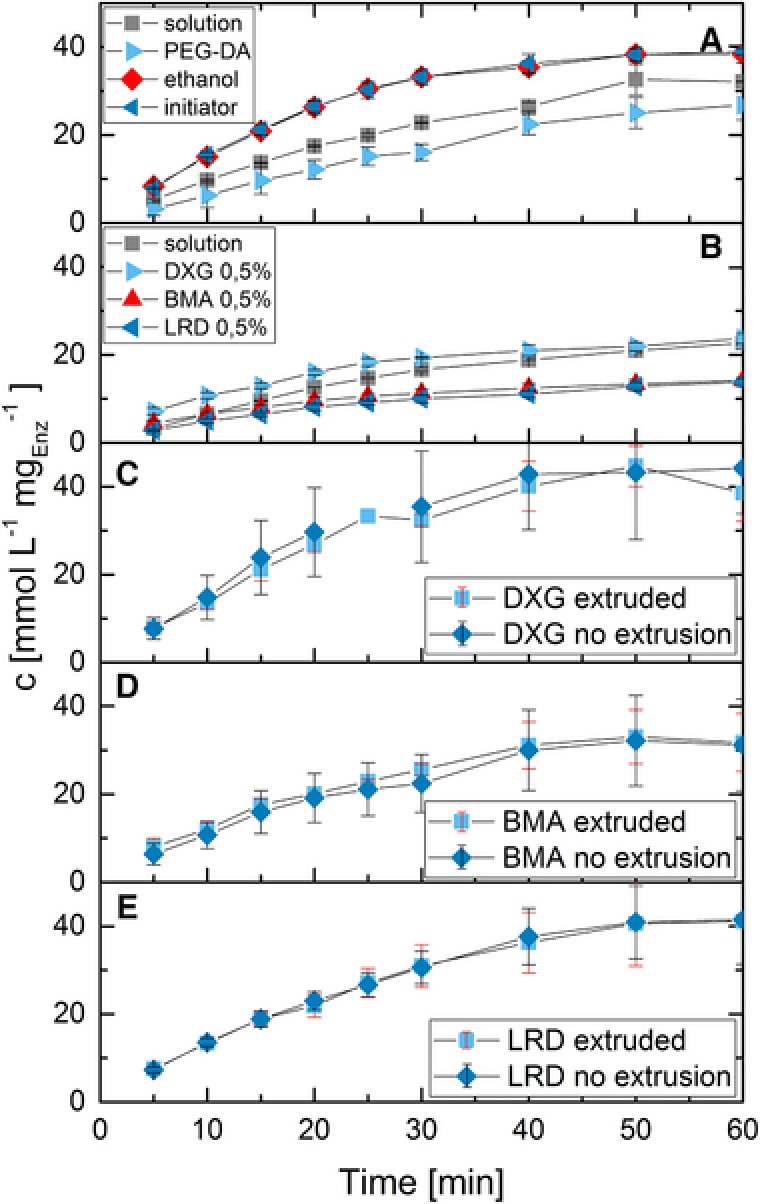
Comparison of enzyme kinetics in hydrogel precursor solutions and hydrogels passing through the extrusion process. (A) Kinetics in the presence of individual components of PEG‐DA hydrogels; (B) Kinetics with the addition of viscosity‐enhancing particles into suspension; (C–E) Activity of enzymes in a ready to use hydrogel mixture before and after extrusion through the printhead of the 3D‐printer. UV‐hardening was omitted and the hydrogel mixture was redissolved in buffer. Resulting concentration of the individual compounds in the runs are as follows (enzyme concentration 10 mg/L in all runs): (A) PEG‐DA 22.3% v/v, ethanol 2.2% v/v, initiator 2.2% v/v; (B) DXG, BMA, and LRD 0.5% w/v. The hydrogel mixtures used in C–E contained 22.3% PEG‐DA, 2.2% initiator solution and 2.5% enzyme stock solution as well as 4.7% DXG (C) respectively 4.7% BMA (D) or 5.0% LRD (E). About 400 mg hydrogel were dissolved per run.
