Figure 4.
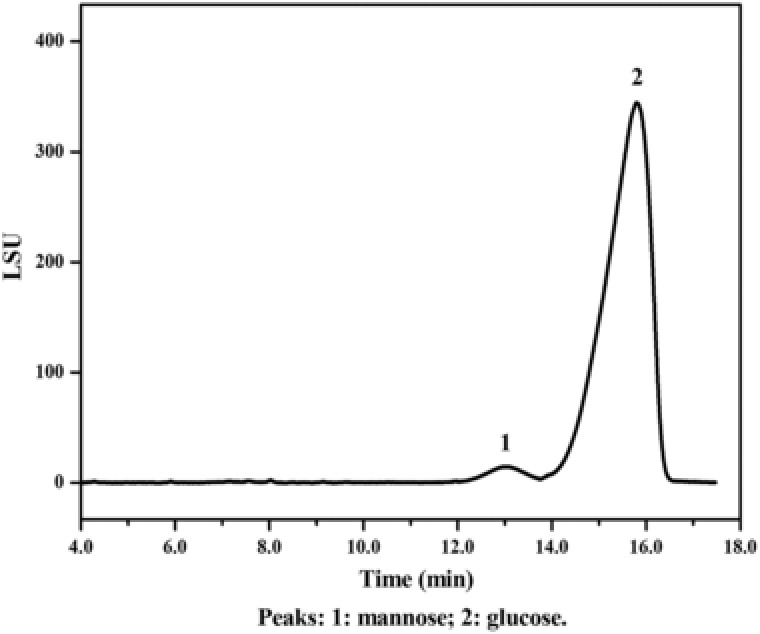
HPLC‐ELSD chromatograph of the polysaccharides isolated and purified from the cell wall of P. pastoris. The yeast cells were treated by induced autolysis, high‐pressure hot‐water treatment, and sonication. The isolated polysaccharide was further purified by isopropanol and papain to remove the residual lipids and proteins, respectively. The purified polysaccharide was treated by sulfuric acid, neutralized by BaCO3 and the content of glucan in the purified product was separated by high‐performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using a Kromasil NH2 (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) HPLC column, with a mobile phase (acetonitrile:H2O = 3:1) and a constant flow rate of 1 mL/min. For ELSD analysis, nitrogen was used as the vehicle gas and the pressure was set at 25 psi. The temperature for the drift tube was set at 40°C. Glucose solution (1 M) and mannose solution (1 M) was used as standards for the analysis.
