Figure 4.
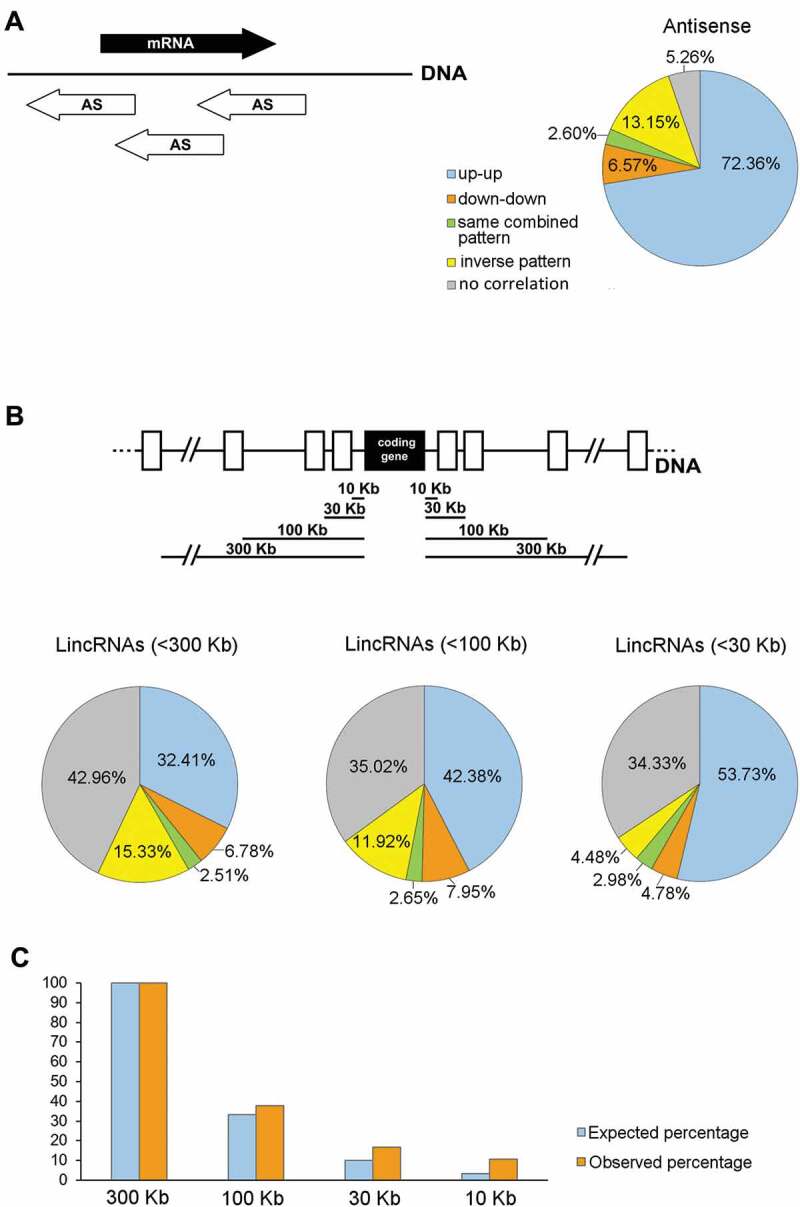
Co-expression of testicular lncRNA genes with protein-coding genes along the different spermatogenic stage transitions. (A) Representation of the percentages of the different co-expression patterns of antisense (AS) lncRNAs and their host protein-coding genes. The schematic diagram shows different positions of overlapping AS lncRNAs (white arrows) in relation to their cognate co-expressed mRNAs (black arrow). Expression patterns were classified as: up-up (both the AS and the coding gene are upregulated); down-down (both the AS and the coding gene are downregulated); same combined pattern (both the AS and the coding gene follow the same combined behaviour along spermatogenesis, e.g. both upregulated at a certain stage transition and then both downregulated at another stage transition, or vice versa); inverse pattern (the AS is upregulated when the coding gene is downregulated, or vice versa); and no correlation (the expression patterns of the AS and the coding gene were not correlatable). (B) Representation of the percentages of the different co-expression patterns of lincRNAs and neighbouring protein-coding genes. The results for gene pairs where the lincRNA is located at <300 Kb, <100 Kb, and <30 Kb distance from the co-expressed coding gene are shown. The top diagram illustrates the different distances at which co-expression patterns between lincRNAs (white rectangles) and protein-coding genes (black rectangle) were analysed. The categories of the expression patterns are the same as in (A). (C) Distribution of the distance of lincRNAs from their co-expressed neighbour coding genes. The number of gene pairs located at <300 Kb from the coding gene is taken as 100%. The percentage of lincRNAs located at varying distances from the coding gene is shown. The expected percentages are those that would be observed at <100 Kb, <30 Kb and <10 Kb, if the distribution was even. For all the co-expression analyses, only those pairs in which both genes were expressed in our transcriptomes and at least one of them was DE, were considered.
