Figure 5. Leishmania susceptibility of IL-1RA−/− BALB/c mice is determined by bone marrow (BM)-derived cells.
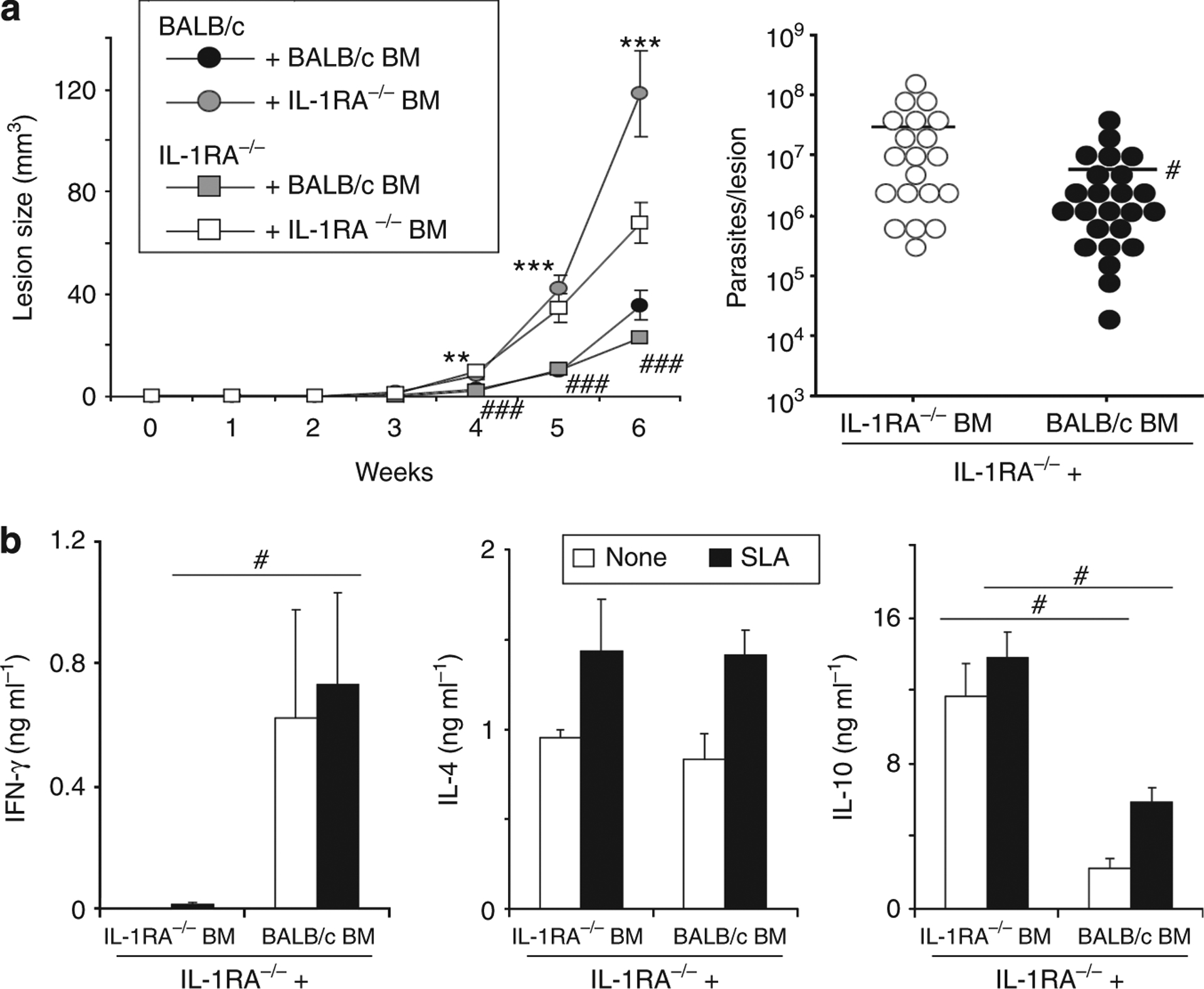
IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA)-deficient or wild-type mice were lethally irradiated with 7 Gy, adoptively transferred with either wild-type or IL-1RA−/− BM (5 × 106 cells per mouse intravenously (i.v.)), and rested for 6 weeks. Subsequently, mice were infected with physiologically relevant low-dose inocula of Leishmania major (103 metacyclic promastigotes). (a) Lesion development was assessed in three dimensions. In week 6, lesional parasite burdens were determined using a limiting dilution assay. Dots represent parasites in individual ears, bars indicate means. (b) In week 6, draining lymph nodes were harvested and restimulated with soluble Leishmania antigen (SLA; 1 × 106 per ml). Cytokine release into 48 hours of supernatants was determined by ELISA. Pooled data from n = 2 independent experiments are shown (mean±SEM; n⩾8, *P⩽0.05, **P⩽0.005, and ***P⩽0.002). * Differences between BALB/c recipient mice; #differences between IL-1RA−/− recipients.
