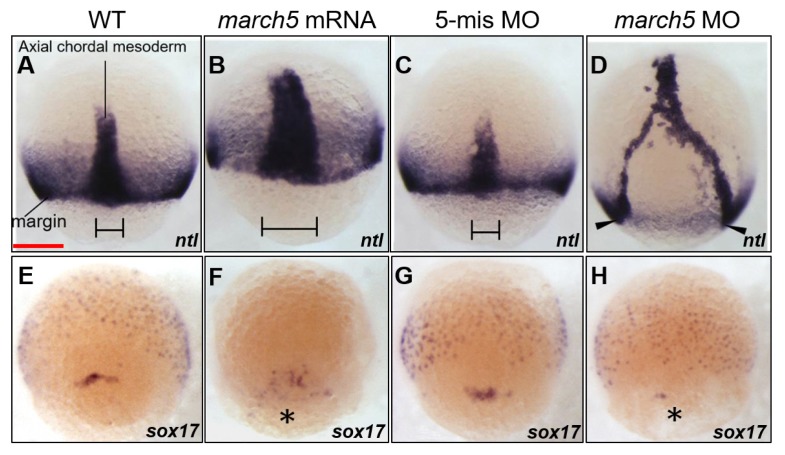
Fig. 4. Knock-down of march5 expression causes changes in expression patterns of the molecular markers, ntl and sox17 at 8 hpf.
(A–D) WISH analysis using ntl as a molecular marker for the convergence and extension (C&E) indicates that loss of march5 function disrupted the processes in C&E governing anterior-posterior patterning. (A) WT embryo. Microinjection of march5 mRNA (50 pg per embryo) into wild-type embryos thickened the C&E (B). march5 5-mismatch control embryos had the similar expression patterns in C&E (C) to that of WT (A). In contrast, knock-down of march5 (0.8 ng morpholino per embryo) splited the body axis (arrowheads) in march5 morphants at 8 hpf (D). (E–H) WISH analysis with sox17 as a molecular marker for the DFCs. sox17 transcripts were present in the DFC of WT (E) and control embryos injected with 5-mismatch (G). Overexpression of march5 (march5 mRNA 50 pg per embryo) extended the area expressing sox17 (F) while knock-down of march5 (0.8 ng of march5 morpholino per embryo) remarkably reduced the level of sox17 transcripts in the DFC (asterisk) of the morphants (H). (A–H) Scale bars = 200 μm.