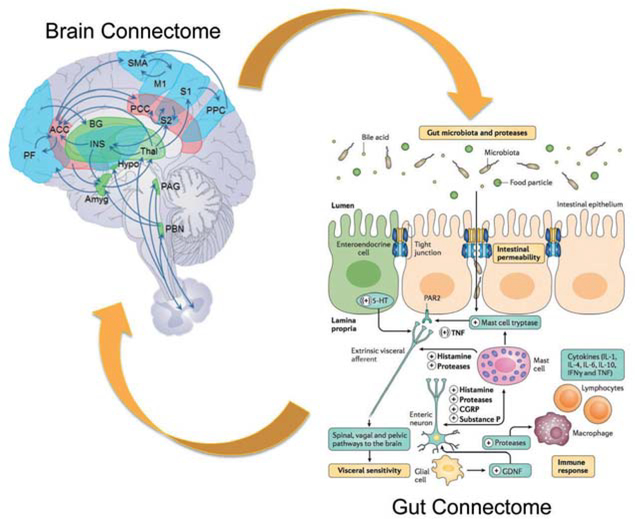
Figure 1.
Proposed integrative model for disorders of gut–brain Interactions. Replacing the conventional focus on individual brain regions and cell types in the gut, this integrative model posits reciprocal interactions between brain networks (brain connectome) and networks made up of multiple cells in the gut, including the gut microbiota (gut connectome). Gut-to-brain communication is mediated by neural, endocrine and inflammatory pathways, while brain-to-gut communication relies mainly on autonomic nervous system output to the gut. Modified with permission from Enck et al.14