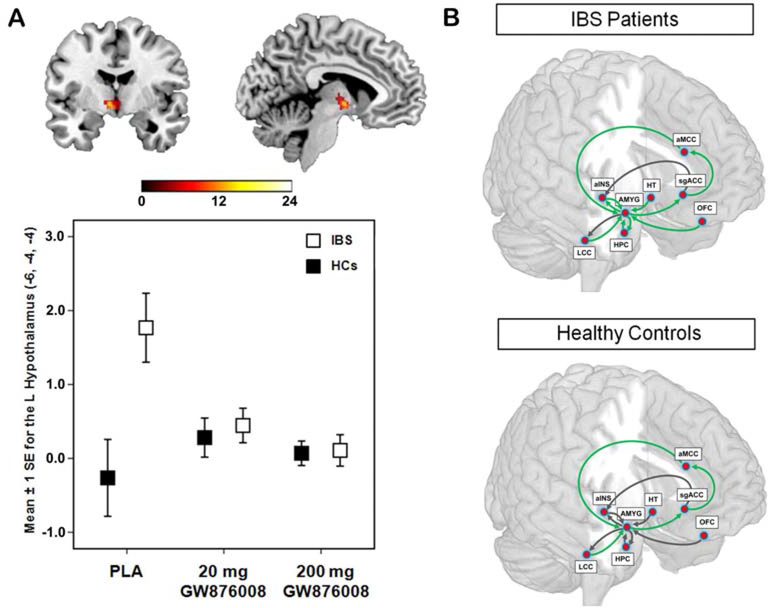
Figure 6.
Effect of a CRF-R1 antagonist on amygdala response and emotional arousal circuit. (A). Error plot showing standard mean errors for beta contrasts (threat – safe) following placebo (PLA) versus a 20 mg or a 200 mg dose of the CRF-R1 antagonist GW876008 for the left locus coeruleus complex in patients with IBS and healthy controls (HCs) during an experimental pain threat. Results show a dose-dependent reduction in the threat-induced amygdala response by the CRF-R1 antagonist. (B). Path coefficients for the effective connectivity analysis of an emotional-arousal circuit during a pain threat following placebo versus high dose of the CRF-R1 antagonist (200 mg GW876008) In healthy controls and IBS subjects. Significantly different parameter estimates are shown by green arrows, while those not significantly different are shown in black. With permission from Hubbard et al.104 alNS, anterior insula; aMCC, anterior midclngulate cortex; AMYG, amygdala; HPC, hippocampus; HT, hypothalamus; LCC, locus coeruleus complex; OFC, orbitomedial prefrontal cortex; sgACC, subgenual anterior cingulate cortex.