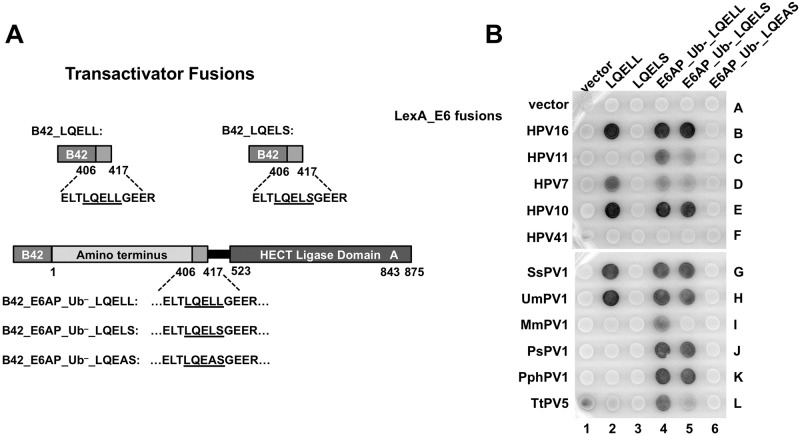
Fig 1. E6 proteins display different E6AP interaction profiles.
(A) Schematic of B42 transactivator-domain E6AP fusion proteins utilized in panel B. B42_LQELL contains E6AP residues 406–417. B42_LQELS also contains E6AP residues 406–417 but the double LL (residues 412 and 413) have been mutated to LS. B42_E6AP_Ub–_LQELL consists of ubiquitin ligase dead full-length E6AP. B42_E6AP_Ub–_LQELS is also ubiquitin ligase dead full-length E6AP, but is mutated in the LQELL motif to LQELS, and similarly B42_E6A_Ub-LQEAS as indicated. (B) E6 proteins from human and animal papillomaviruses have different requirements for interaction with E6AP. Bait yeast strains expressing the LexA DNA binding domain fused to E6 proteins from the listed papillomaviruses were mated to prey yeast expressing B42 transcriptional activation domain fusions illustrated in part A. HPV41 E6 preferentially binds MAML1 and not E6AP, and was used as a negative control for binding. The horizontal white line indicates development on parallel matched XGAL plates. H = Homo sapiens (human), Ps = Phocoena spinipinnis (Burmeister’s porpoise), Pph = Phocoena phocoena (harbor porpoise), Tt = Tursiops truncatus (bottlenose dolphin), Mm = Macaca mulata (rhesus monkey), Ss = Sus scrofa (wild boar), Um = Ursus maritimus (polar bear).