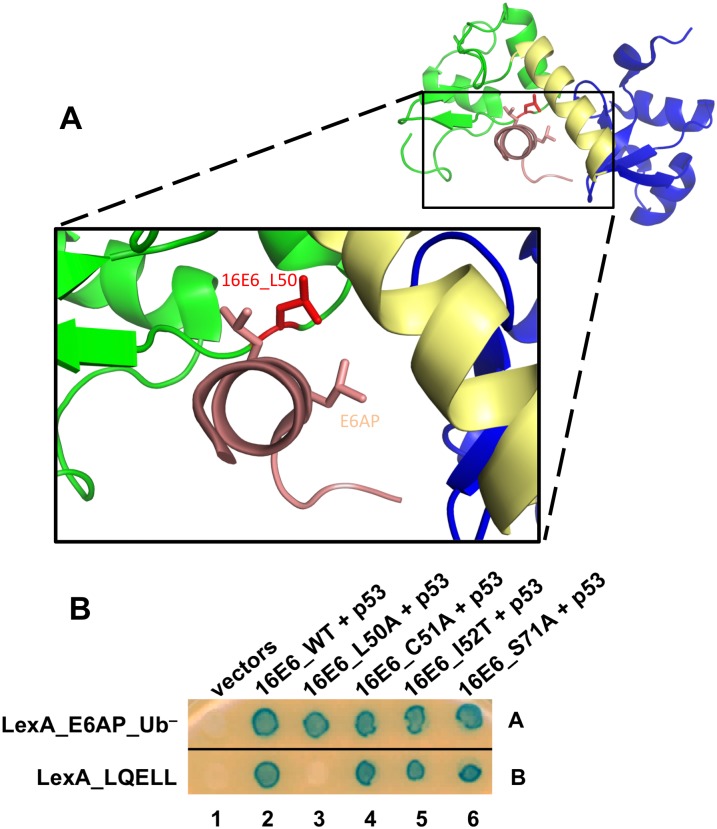
Fig 2. The 16E6_L50A mutant enables characterization of E6-E6AP interactions.
(A) The E6 L50 residue is in close proximity to the double L residues in the E6AP LQELL peptide. The HPV16 E6 structure (PDB file 4GIZ) is depicted with the amino terminal zinc-structured domain in green, the carboxy terminal zinc-structured domain in blue, and the connecting alpha helix in yellow. The 16E6 protein is shown interacting with the E6AP LQELL peptide (in light pink), and the side chains of the double L residues are shown. The side chain of the E6 L50 residue is highlighted in red. The E6 L50 residue (red) makes a 3.7 Å side chain contact with the last leucine residue (L) in the E6AP LQELL peptide which is lost upon mutation of L50 to an alanine. (B) Mutation of 16E6 L50 residue to an alanine results in a high-risk E6 protein that is unable to bind the isolated E6AP LQELL peptide but retains association with full-length E6AP. Bait Yeast expressing LexA fused to either full length ubiquitin ligase dead E6AP (E6AP_Ub–) or the isolated E6AP LQELL peptide (E6AP_406–417) were mated to yeast co-expressing untagged 16E6_WT or the indicated 16E6 mutants containing a single amino acid change and p53.