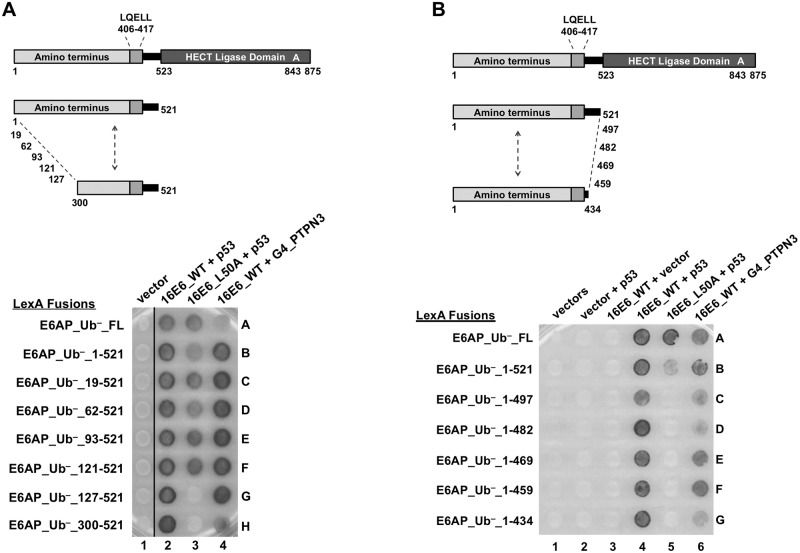
Fig 10. E6AP regions in addition to the LQELL motif in both the amino and carboxy terminus are important in mediating 16E6 binding.
(A) E6AP residues 121–127 are important for enabling 16E6_L50A interaction and p53 recruitment. At the top, there is a schematic of E6AP and E6AP truncation mutants with yeast hybrid associations shown below. E6AP amino terminal truncations lack the HECT ligase domain, but retain the LQELL E6 binding motif. The indicated yeast expression plasmids were introduced into a LexA-responsive reporter strain by mating. Co-expression of 16E6_WT and p53 with each LexA_E6AP serves as a positive control for E6AP expression and folding. Co-expression of Gal4 (G4) transactivator fused PTPN3 with 16E6_WT and the various LexA_E6AP truncations ensures that 16E6_WT is being expressed and can recruit the PDZ protein PTPN3 to the E6AP protein. Vertical black line indicates removal of irrelevant samples. (B) E6AP residues 521–497 are important in mediating 16E6_L50A interaction with E6AP to recruit p53. At the top is a schematic of E6AP and E6AP truncation mutants examined for interaction with 16E6_L50A + p53. E6AP truncations lack the HECT ligase domain but retain the LQELL E6 binding motif. Yeast containing three hybrid plasmids expressing the indicated proteins were mated, selected, and analyzed for interaction as in part A. The PDZ protein PTPN3 co-expressed with 16E6_WT and each E6AP truncation demonstrated ability of 16E6 to bind the E6AP protein and recruit PTPN3.