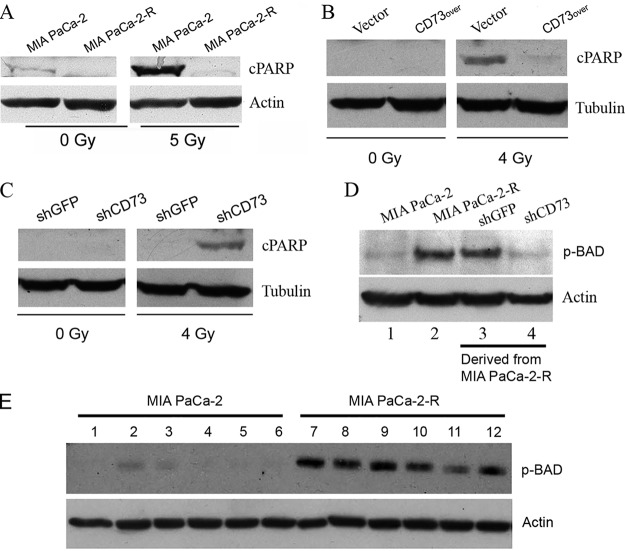
Fig. 6.
CD73 enhances resistance to IR-induced apoptosis and promotes BAD phosphorylation at Ser-136. A, The radioresistant cells are more resistant to IR-induced apoptosis than the parental cells. B, Ectopic overexpression of CD73 enhances resistance to IR-induced apoptosis. C, Knockdown of CD73 re-sensitizes the radioresistant cells to IR-induced apoptosis. The indicated cells were treated with the indicated doses of γ-radiation. After 48 h of recovery culture, cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. D, Western blot analysis of BAD Ser-136 phosphorylation in the indicated cells. shGFP cells and shCD73 cells were derived from MIA PaCa-2-R cells. E, Effect of various kinase inhibitors on BAD Ser-136 phosphorylation. MIA PaCa-2 and MIA PaCa-2-R cells were mock-treated (lanes #1 and 7) or treated with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (#2 and 8), dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 (#3 and 9), AKT inhibitor MK-2206 (#4 and 10), NVP-BEZ235+MK-2206 (#5 and 11) or MK-2206+LY294002 (#6 and 12) for 24 h, and lysates of the cells were analyzed by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. Vector, CD73over, shGFP, and shCD73 cells, see Fig. 5 legend. cPARP, 85 kDa fragment of cleaved PARP. Actin and tubulin were used as loading controls.