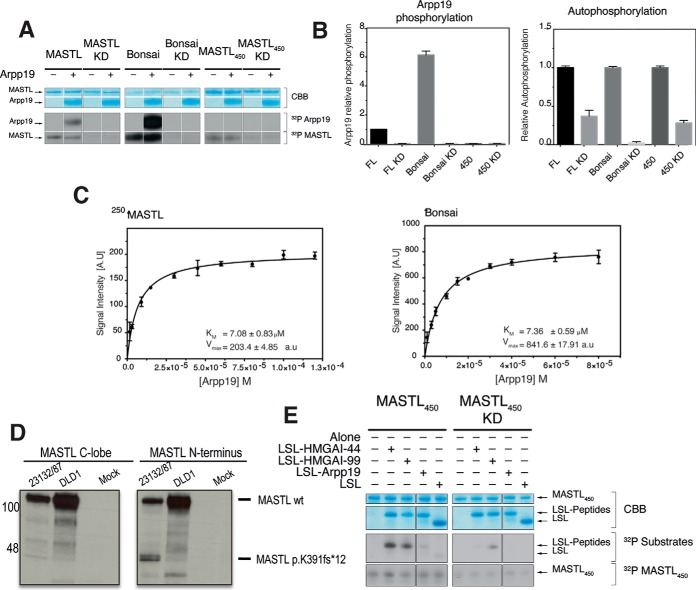
Fig. 2.
Kinase activity assays. In vitro kinase assay for MASTL, Bonsai and MASTL450 activity. A, MASTL, Bonsai and MASTL450 proteins and their corresponding kinase-dead mutants were purified from HEK293 cells (interphase cells) and used for in vitro kinase assays using Arpp19 as a substrate. After 30 min at 30 °C, the kinase reaction was stopped with LDS sample buffer. Autoradiograms display the incorporation of (32P) in Arpp19 (substrate phosphorylation) and the MASTL proteins (autophosphorylation). MASTL and Bonsai readily phosphorylated Arpp19. Bonsai's Arpp19-phosphorylation and autophosphorylation levels were increased when compared with the MASTL protein. B, Densitometric analysis of the relative Arpp19-phosphorylation and autophosphorylation levels of MASTL, Bonsai and MASTL450, respectively. Bonsai phosphorylates six times more Arpp19 than MASTL. Analysis comes from several independent experiments (n = 3). Error bars display the standard error of the mean (S.E.). C, Kinetic parameters (Km and Vmax) for MASTL (left panel) and Bonsai (right panel) using different Arpp19 concentrations as substrate. Bonsai again display an increased ability to phosphorylate Arpp19. Non-linear regression of the data (10 different Arpp19 concentrations, see supplemental Fig. S4) was calculated (n = 3 for each of the 10 Arpp19 concentration) and plotted by the built-in enzyme kinetics module of the GraphPad PRISM 6.0 software. Error bars display the standard deviation (S.D.) calculated by the statistic software. D, Detection of MASTL peptides in the human gastric carcinoma cell line 23132/87 (carrying a heterozygous p.K391Nfs*12 mutation) and the colorectal cancer cell line DLD1 (wild-type for MASTL). Protein lysates from asynchronous 23132/87 and DLD1 cells were immunoprecipitated with the MASTL antibody 159B and MASTL bands were detected with antibodies specific for the C-lobe (left) and N terminus (268F clone; right). Mock refers to immunoprecipitations in the absence of lysates. The arrow indicates the short MASTL peptide excepted from the p.K391Nfs*12 mutation. E, MASTL450 and MASTL450 KD in vitro kinase assay with LSL-HMGAI, -Geminin and -Arpp19 peptides as substrate. MASTL450 can phosphorylate the LSL-HMGAI (S-44 and S-99) peptides, whereas it was unable to phosphorylate either the LSL-Geminin or -Arpp19 peptides.