Figure 3.
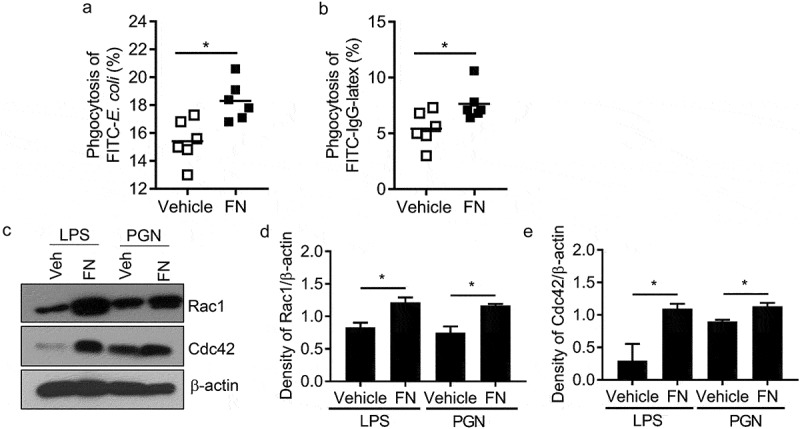
FN functions as an opsonin for macrophage phagocytosis. The effect of FN in macrophage phagocytosis to FITC conjugated E. coli was analyzed by FACS (a). Briefly, peritoneal macrophages from WT mice and bacteria were mixed in suspension at a ratio of 1:10 (cell: bacteria) with and without FN. FITC-E. coli positive cell of macrophages was analyzed by FACS (a); FcγR-mediated phagocytosis of macrophages was also analyzed by FITC-IgG latex beads with/without FN (b). Peritoneal macrophages were cultured on glass coverslips and incubated with IgG-coupled latex at a ratio of 1:10 for 15–30 min at 37°C to assay phagocytosis. Phagocytosis was assessed by detecting the percent of the FITC+ cells by FACS. n = 6. ∗, p < 0.01. FN promotes expression of total Rac1 and Cdc42 proteins in peritoneal macrophages after stimulation with LPS and PGN, as determined by Western blot analysis (c). The cells lysates were fractionated by 12% SDS-PAGE gel. Expression of actin serves as a loading control and density of Rac1/β-actin and (d) Cdc42/β-actin (e) was quantified with Image J software. (n = 3, *p < 0.05). Statistical comparisons among treatment groups were performed by randomized-design two-way ANOVA, followed by unpaired Student’s t-test for two groups using Prism software (Graph Pad Inc., La Jolla, CA). Statistical significance was defined as a P value of less than 0.05.
