Figure 1. cAMP signaling switches cDC2s to a pro-Th17 bias.
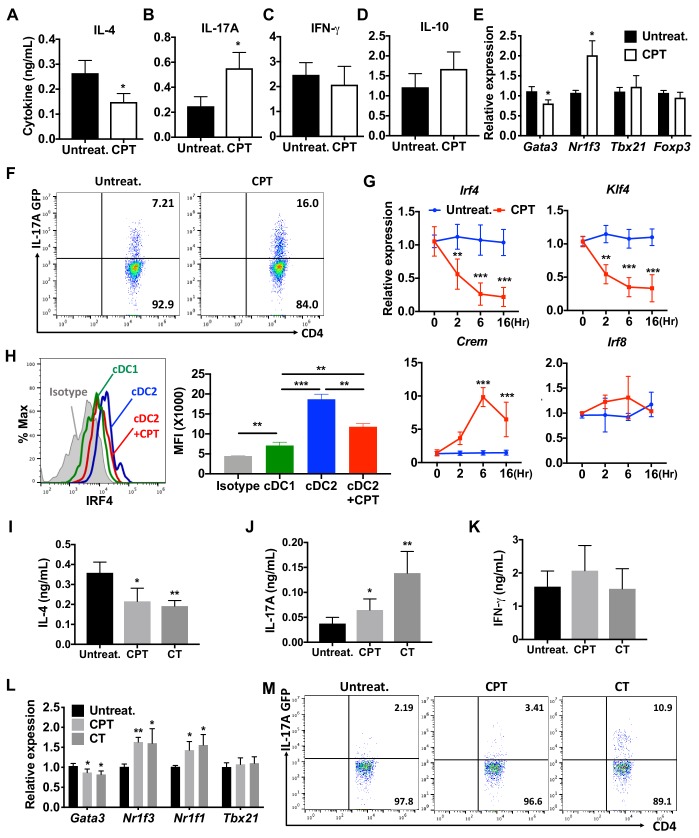
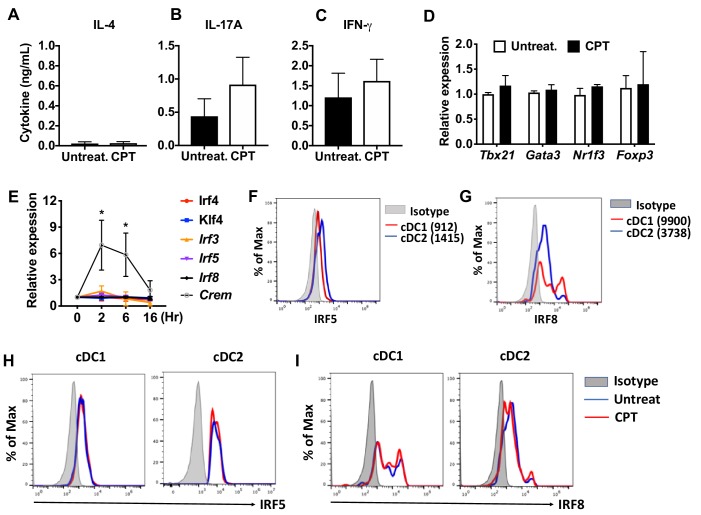
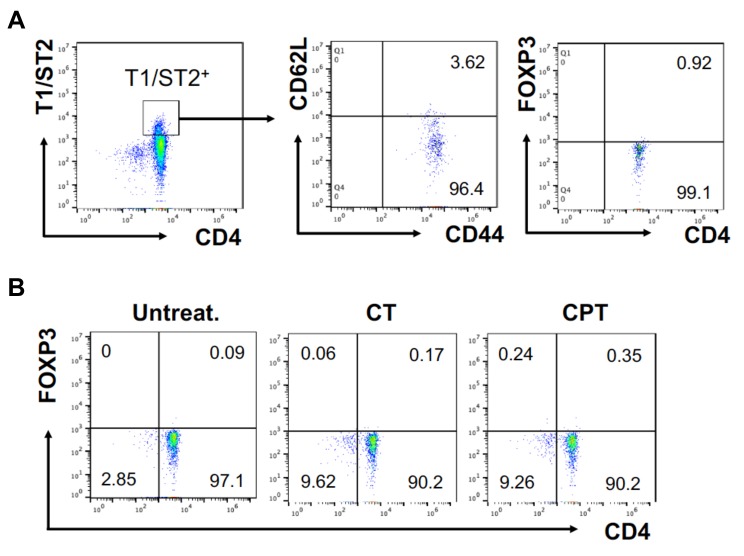
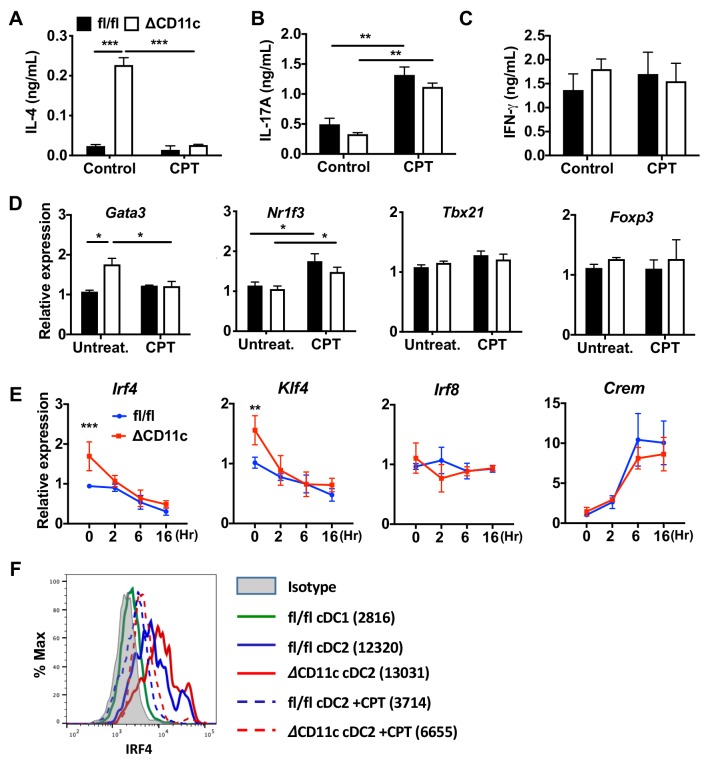
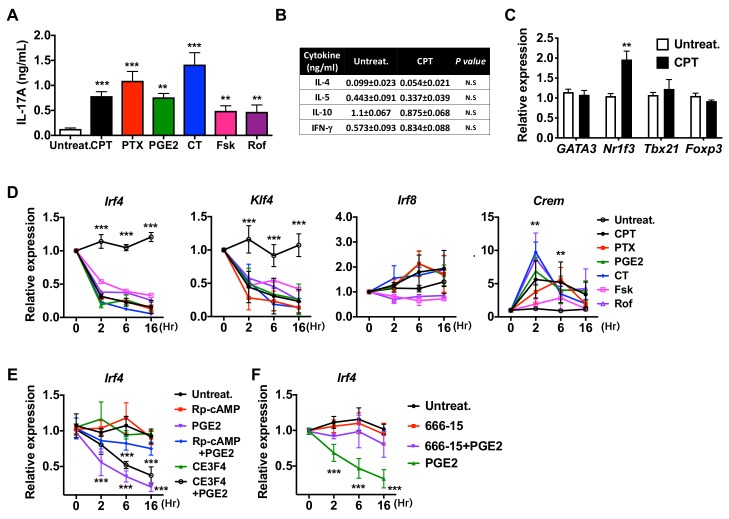
(A–D) IL-4, IL-17A, IFN-γ and IL-10 levels from anti-CD3/28 Ab-stimulated OT-II cells co-cultured with WT splenic cDC2s (CD11c+CD11b+CD8α-) pretreated with or without CPT. (E) qPCR analysis of lineage commitment factors in OT-II T cells co-cultured with WT cDC2s in the presence of CPT. (F) GFP expression from IL-17GFP OT-II CD4+ T cells co-cultured with WT cDC2s pretreated with or without CPT. (G) qPCR of TFs in WT cDC2s treated with CPT (50 μM). Two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test; n = 3 in each group, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Effect of CPT treatment; Irf4 (p=0.002), Klf4 (p<0.001) and Crem (p<0.001). (H) Intracellular staining of IRF4 in WT cDC1 and cDC2s treated with or without CPT for 48 hr. (I–M) Fate mapping: IL-17GFP OT-II CD4+ T cells were co-cultured with GnasΔCD11c BM-APCs to generate memory Th2 cells (1st co-culture). From the 1st co-culture, T1/ST2+ cells were FACS sorted and then used for co-culture with WT cDC2s pretreated with or without CPT or Cholera toxin (CT) (2nd co-culture). (I) IL-4, (J) IL-17A and (K) IFN-γ levels, (L) qPCR of lineage commitment factors, and (M) GFP signal for IL-17 expression in the re-stimulated CD4+ T cells from 2nd co-culture. Data are representative of three independent experiments; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.