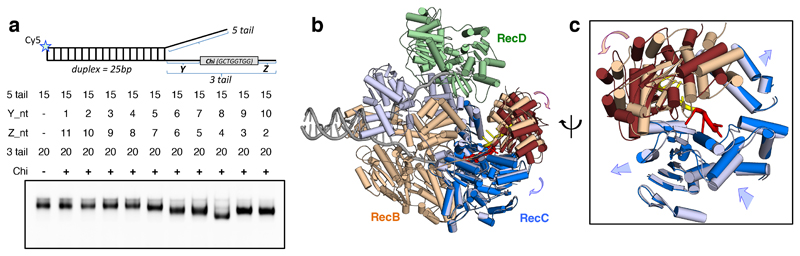
Fig. 1. Structural changes associated with Chi binding.
a, Native gel mobility shift assays (bottom) show an altered shift of the RecBCD-DNA complex band when the substrate contained eight bases between the fork junction and the Chi sequence (Y = 8), suggesting a Chi-specific conformational change. In the schematic on top, the star indicates position of the Cy5 fluorescent label. b, Overview of the conformational changes between the Chi-recognised and the Chi-unrecognised states. The two structures were superimposed on the RecB motor domains. The unchanged domains of both structures are shown in the same colours: RecB in wheat, RecC in light blue and RecD in pale green. The areas that undergo large conformational changes in the Chi-recognised state are coloured darker: RecB nuclease domain in brown and RecC helicase-like domains in blue. The Chi sequence is coloured red and the four bases after Chi are yellow, with the rest of the DNA in grey. c, Expanded and rotated view to emphasise the conformational changes in RecC and RecB nuclease domain around Chi (red). Arrows indicate direction of movements.