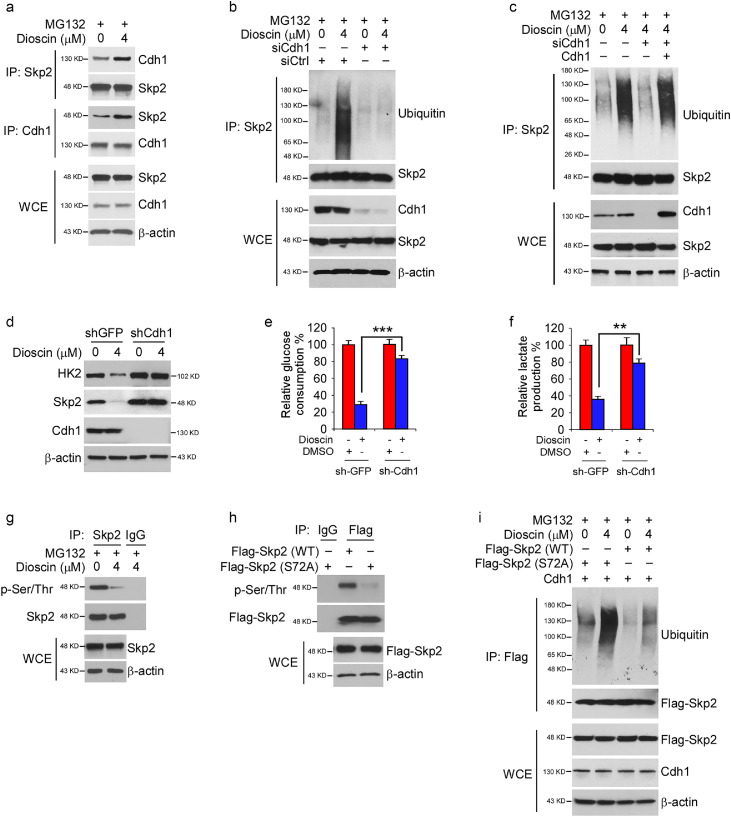
Fig. 5.
Cdh1 is required for dioscin-induced Skp2 ubiquitination. (a) HT29 cells were treated with dioscin for 24 h, WCE was subjected to co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) analysis. (b) HT29 cells were transfected with siCtrl or siCdh1 and treated with DMSO or dioscin for 24 h, followed by MG132 treatment for another 6 h, WCE was collected and subjected to in vivo ubiquitination assay. (c) HT29 cells were transfected with siCtrl or siCdh1 for 24 h. The siCdh1 transfected cells were overexpressed with Cdh1 and treated with DMSO or dioscin for 24 h, followed by MG132 treatment for another 6 h. WCE were subjected to in vivo ubiquitination assay. (d–f) HT29 cells stable expression of shGFP or shCdh1 were treated with DMSO or dioscin for 24 h, WCE was subjected to IB analysis (d). Glucose consumption (e), and lactate production (f) were examined in the cell culture medium. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. (g) HT29 cells were treated with DMSO or dioscin for 24 h, WCE was collected and subjected to co-IP assay, followed by IB analysis. (h) HT29 cells were transfected with Flag-Skp2 WT and Flag-Skp2 (S72A) mutant for 48 h, WCE was subjected to co-IP assay followed by IB analysis. (i) HT29 cells were transfected with the constructs as indicated for 24 h, cells were then treated with DMSO or dioscin for 24 h, followed by MG132 treatment for 6 h, WCE was subjected to in vivo ubiquitination assay.