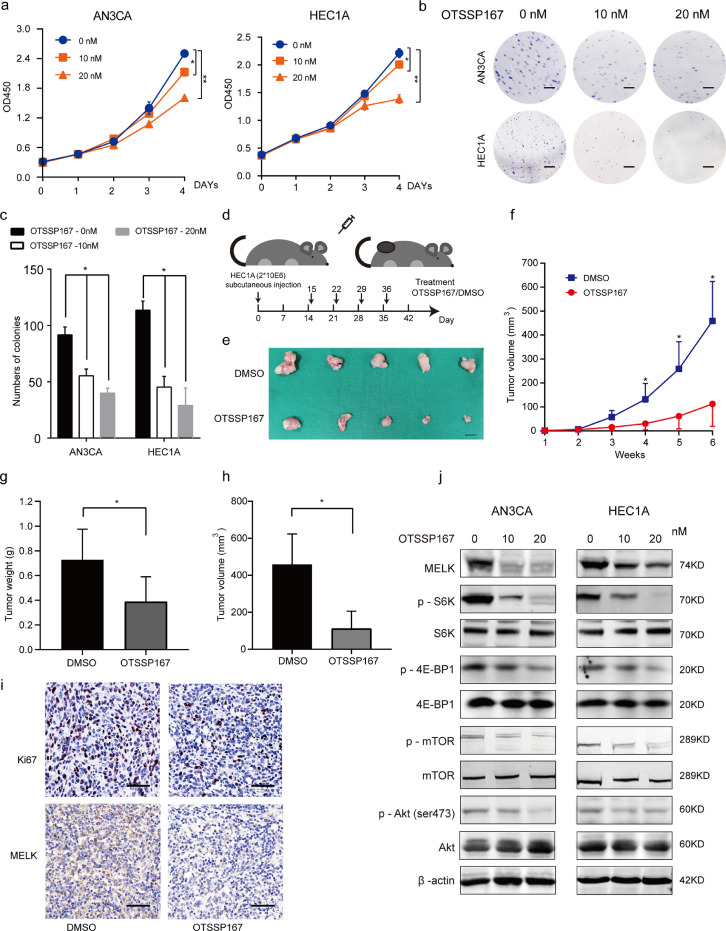
Fig. 6.
OTSSP167 inhibits cell proliferation by inhibiting MELK and thus mTORC1 and −2 signaling. a. CCK-8 assays were conducted to detect cell proliferation after treatment with 10 and 20 nM OTSSP167. Values are means ± SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01(student's t-test). b. The colony formation assay was performed to assess the cell proliferation capability after treatment with 10 and 20 nM OTSSP167 in EC cells (AN3CA and HEC1A). Scale bar, 5 mm. c. The representative photographs of the colony formation assay are shown. Values are means ± SD, n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01(student's t-test). d. Schematic presentation of the animal study treated with OTSSP167. e. The representative images of tumors on day 42 after treatment of HEC1A xenograft mice. Scale bar, 50 mm. f. Growth curve of tumors treated with OTSSP167. Values are means ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01(student's t-test). g. statistical analysis of tumor weight growth over 6 weeks. Values are means ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01(student's t-test). h. statistical analysis of tumor volume over 6 weeks. Values are means ± SD, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01(student's t-test). i. Representative images of Ki67 staining and MELK staining in xenograft tumors from OTSSP167-treated groups and DMSO control groups. Scale bar, 50 μm. j. Western blotting analysis of MELK and phosphorylated and total S6K, 4E-BP1, mTOR, and AKT during treatment with 10 or 20 nM OTSSP167. β-actin served as the loading control.