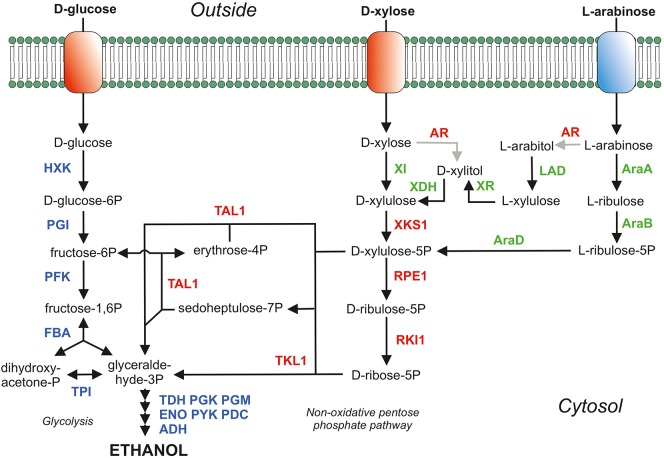
Figure 1.
Main sugar consumption pathways in S. cerevisiae. The proteins depicted in blue belong the glycolysis and ethanol production (fermentation). Proteins in red are homologous over-expressed proteins of the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) and AR; the aldose/xylose/arabinose reductase (EC:1.1.1.21) which is over-expressed in the yeast strains expressing XDH (xylitol dehydrogenase; EC:1.1.1.9) but is deleted in yeast strains expressing XI (xylose isomerase; EC:5.3.1.5). In green are depicted the heterologously over-expressed proteins to metabolize D-xylose (XI and XDH) and the proteins for L-arabinose metabolism [AraA (isomerase; EC:5.3.1.4), AraB (ribulokinase; EC:2.7.1.16) and AraD (epimerase; EC:5.1.3.4)]. To prevent arabitol formation in an L-arabinose consuming yeast strain expressing the AraBAD pathway the AR (aldose reductase; EC:1.1.1.21; gre3 gene) was deleted. The AR was, however, over-expressed in the L-arabinose pathway expressing LAD (L-arabinitol 4-dehydrogenase; EC:1.1.1.12) and XR (L-xylulose reductase; EC:1.1.1.10). Adapted from De Waal P.P., patent WO2003/062430 and WO2008/041840, with permission.