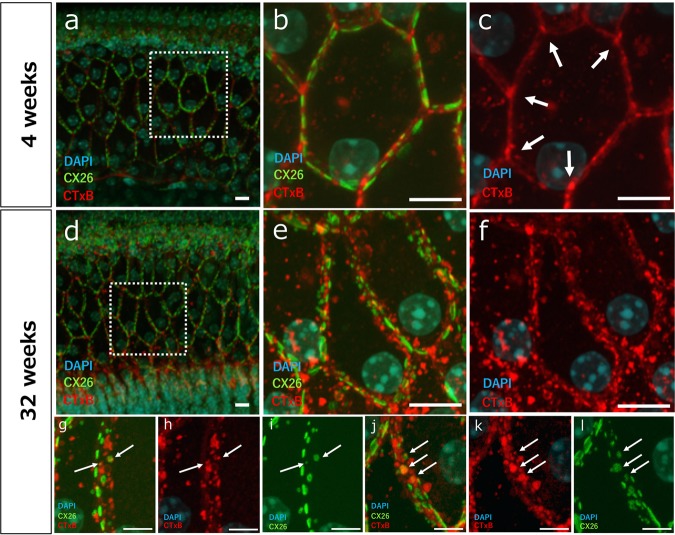
Fig. 5. Changes in the distribution of lipid rafts around degraded GJPs of ISCs in 32-week-old mice and the process of degradation of GJPs.
Lipid rafts were stained in cochleae from 4- and 32-week-old mice using CTxB (red) and were counterstained with anti-Cx26 (green) and DAPI (blue). a, b In 4-week-old mice, lipid rafts were observed between GJPs. d, e In 32-week-old mice, lipid rafts were scattered around degraded GJPs with no regularity. Focusing on the distribution of lipid rafts, in 4-week-old mice (c), lipid rafts localize mainly at multicellular junction sites between adjacent GJPs. Arrows in c indicate the accumulation of lipid rafts adjacent to normal GJPs. In 32-week-old mice (f), lipid rafts contributed to the irregularly around GJPs. g, j Representative images of the cell borders of cochlear supporting cells in 32-week-old mice. As Cx26 became increasingly hydrophobic with age, lipid rafts were observed around GJPs (h and k), and some GJPs were colocalized with lipid rafts (i and l) and fragmented. Arrows in (g–l) indicate the colocalization between lipid rafts and GJPs. Scale bars indicate 10 μm (a–f) and 5 μm (g–l).