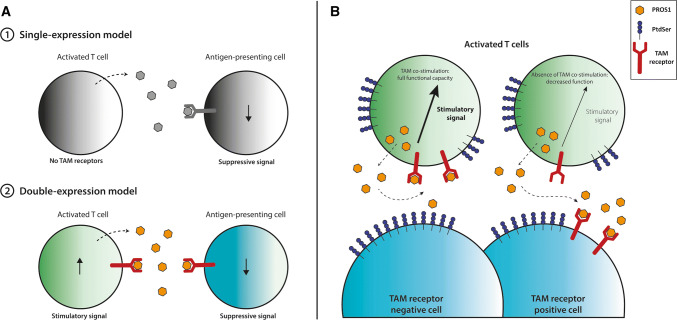
Fig. 1.
Consequences of TAM receptor signaling on T cells and competing cells. a Previously, T cells were thought to express PROS1, but not TAM receptors. PROS1 secretion by T cells subsequently resulted in a negative feedback loop to the APC. In the double-expression model, T-cell secreted PROS1 serves as an auto-stimulatory signal for the T cell and an inhibitory signal for the APC. b Activated T cells express PROS1, TAM receptors, and PtdSer. When the T cell encounters a TAM receptor negative cell, PROS1 will activate MERTK on the T cell. When the T cell encounters another TAM receptor positive cell, PROS1 will be competed for, as APCs and cancer cells express high amounts of TAM receptors. T cell-produced PROS1 will subsequently activate the other TAM receptor-positive cell (APC, cancer cell) and T cells will lose the PROS1-MERTK costimulatory signal. PROS1 Protein S, PtdSer phosphatidylserine, TAM receptor TYRO3, AXL, MERTK receptor family