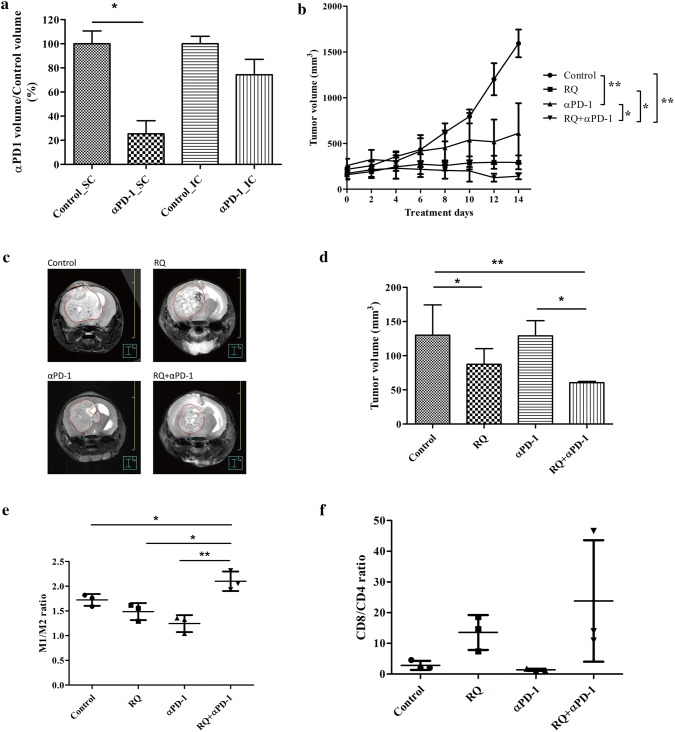
Fig. 5.
In vivo efficacy evaluation of combined RQ and anti-PD1 treatment in GL261 xenograft models. a Comparison of anti-PD-1 inhibition of tumor growth in subcutaneous (SC) and intra-cranial (IC) GL261 mice models. IC tumor was not as effective as SC tumor to anti-PD-1 treatment. b Growth inhibition curve of SC GL261 tumor model. Each data point represents the average tumor burden of 6 mice. c The representative photograph of T2-weighted FSE MRI scans of orthotropic GL261 intra-cranial tumor model. MRI images of GL261 were acquired 16 days following IC implantation of 2 × 105 GL261 cells. The tumor size of each group of tumor-bearing mice was assessed by 7T micro PET/MRI T2-weighted FSE imaging (n = 4 mice/group). d Volumetric assessment of the glioma in different treatment groups (n = 4). (Error bars, mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). GL261 orthotropic mice were sacrificed on 14th day for all treatment groups and flow cytometry was used to analyze e M1 to M2 ratio, f ratio of CD8 to CD4 T cells (n = 4). (Error bars, mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)