FIGURE 3.
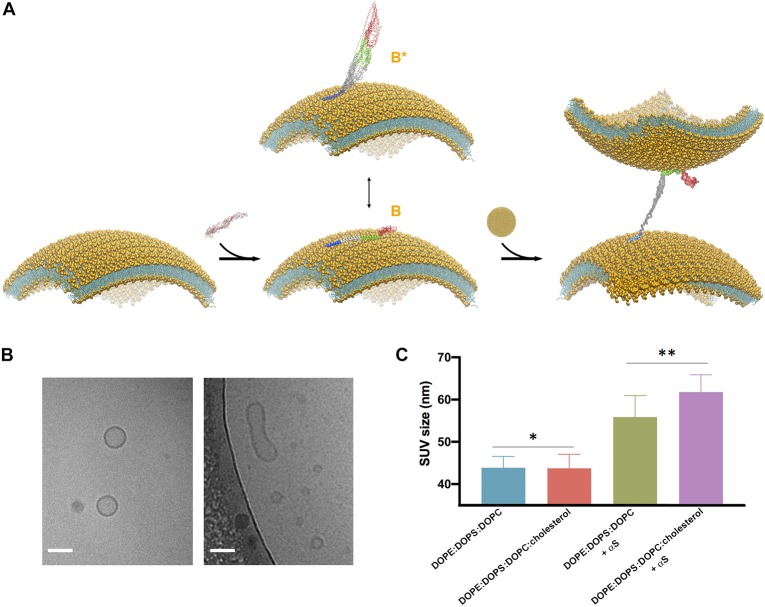
Cholesterol enhances vesicle-vesicle interactions promoted by αS. (A) Schematic representation of the SUV binding modes of αS and the double-anchor mechanism for vesicle-vesicle interactions (Fusco et al., 2016b). Upon binding to acidic SUVs, αS adopts an ensemble conformation (center). Two major conformational states are shown in the scheme, namely a fully α-helical state spanning the whole region 1–97 (state B) bound to the same membrane and a state B∗ that interacts with the membrane exclusively through the N-terminal anchor (residues 1–25), with the rest of the protein being detached from the membrane surface. The state B∗ is an active conformation for the recruitment of a second vesicle through the double-anchor mechanism (Fusco et al., 2016b) (right), with a single αS molecule binding two vesicles via its N-terminal region (lower vesicle) and the region 65–97 (upper vesicle). The population of B∗ measured using CEST experiments was found to increase from 38% to 51% when interacting with SUV-0% and SUV-31%, respectively. Color codes for the regions of αS are blue (1–25), gray (26–64), green (65–97), and red (98–140). (B) Examples of isolated (left) and fused (right) SUV-31%, as probed from images obtained in vitro by cryo-EM, the scale bar is 50 nm. (C) DLS measurements of SUVs, either isolated or incubated with αS. Samples used in DLS measurements were incubated, with or without αS molecules, for 1 h at 298 K using freshly prepared SUVs at a concentration of 0.05% and made with SUV-0% and SUV-31%. The SUV concentrations were calculated by considering the DOPE:DOPS:DOPC component exclusively in both types of vesicles. In order to compensate for the 2.6 difference in KD, the concentrations of αS when incubated with SUV-0% and SUV-31%, were 77 μM and 200 μM, respectively, which enables to decouple the differences in the binding affinities from the tendency to promote vesicle fusion. Each measurement was made of 10 replicates. Error bars report standard deviations of the centers of the size distributions in the 10 replicates. The single (*) and double (**) asterisks indicate P = 0.9264 and P = 0.01, respectively. These were calculated using the unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction (Sawilowsky, 2002).