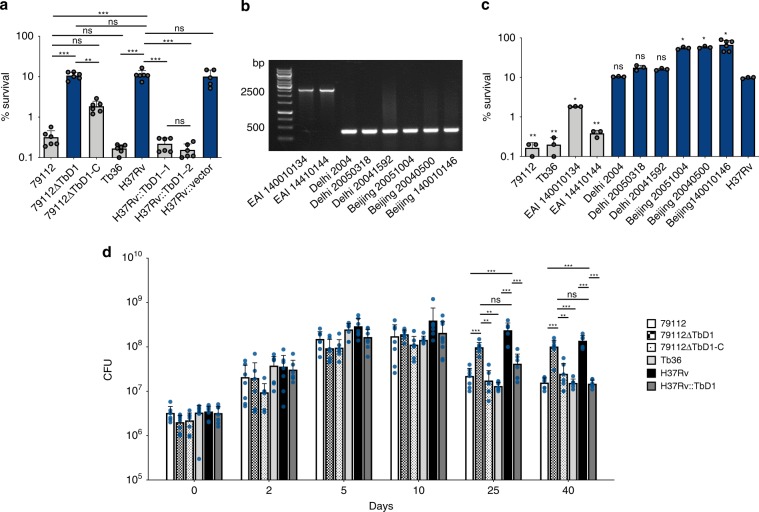
Fig. 7. Impact of TbD1 on Mtb sensitivity to oxidative stress and hypoxia.
a Survival percentages of WT 79112 and Tb36 ancestral TbD1-intact strains or modern Mtb H37Rv, in comparison with those of TbD1-deleted or TbD1-complemented derivative strains after 1-h exposure to 10 mM H2O2. An H37Rv strain complemented with the empty vector was included in the assay as an additional control. The susceptibility of each strain was expressed as percentage of survival relative to the time 0. The figure depicts single data points, mean and standard deviation of survival percentages obtained for each strain in six independent bacterial cultures. b, c Sensitivity profiles of a panel of Mtb clinical isolates belonging to different lineages, harboring or not an intact TbD1 locus. b Amplicons obtained by PCR analysis on genomic DNAs from different Mtb isolates, by using primers specific for the TbD1-flanking regions. c Survival percentages of clinical isolates after exposure to H2O2. Mtb 79112, Tb36 and H37Rv were also included as control strains. In a, c TbD1-intact strains are indicated by gray bars, while TbD1-deleted strains are indicated by blue bars. The graph represents single data points, mean and standard deviation of survival percentages obtained for each strain in a representative experiment performed in triplicate (6 bacterial replicates were testes for the Beijing 140010146 strain). d Growth and survival of Mtb TbD1-intact and TbD1-deleted strains in the Wayne dormancy culture system. All strains were grown in Dubos medium without glycerol, in sealed 30 ml tubes (liquid volume: air volume ratio of 2:1). After 2, 5, 10, 25, and 40 days of incubation at 37 °C the CFU numbers were determined. The panel shows the single data points, mean and standard deviation of CFU values recovered for each strain in seven independent growth/survival assays. Statistical significance of differences in survival percentages (a, c) or in CFU values (d) determined by one-way Anova with Bonferroni post hoc test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ns: not significant) are shown. In c only the statistical significance of differences in survival percentages between different clinical isolates and the H37Rv reference strains is depicted.