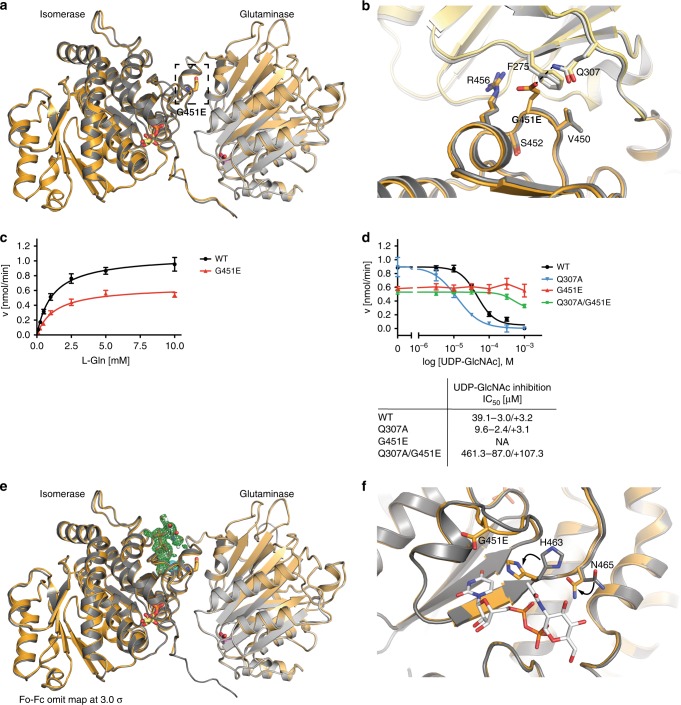
Fig. 5. GFAT-1 gain-of-function mutation perturbs UDP-GlcNAc inhibition.
a, b Effect of G451E mutation on GFAT-1 structure. Proteins are presented as cartoons. Superposition of wild type GFAT-1 (light gray/dark gray) and G451E GFAT-1 (yellow/orange). Glc6P (yellow sticks) and l-Glu (violet sticks) are highlighted. a G451E (sticks) is located at the isomerase domain of GFAT-1 pointing towards the interdomain linker (black box). b Superposition of the wild type and the G451E GFAT-1 structure focusing on residues in close proximity to the mutation. c l-Gln kinetic of wild type (WT, black circle) and G451E (red triangle) GFAT-1 (mean ± SEM, n = 5). d Representative UDP-GlcNAc inhibition of wild type (black circle), G451E (red triangle), Q307A (blue triangle), and Q307A/G451E (green square) GFAT-1 (mean ± SD, n = 3). Table: IC50 UDP-GlcNAc values (mean ± SEM, n = 3). e, f Superposition of UDP-GlcNAc-bound G451E GFAT-1 (yellow/orange) and wild type GFAT-1 in the absence of UDP-GlcNAc (gray). Proteins are presented as cartoons. Glc6P (yellow sticks), l-Glu (violet sticks), UDP-GlcNAc (white sticks), Mg2+ (cyan sphere), and G451E (sticks) are highlighted. e Overall structure with Fo−Fc omit map (green) of UDP-GlcNAc binding to G451E GFAT-1 at a contour level of 3.0 RMSD. f Close-up of the UDP-GlcNAc-binding pocket with local side chain movements in G451E GFAT-1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.