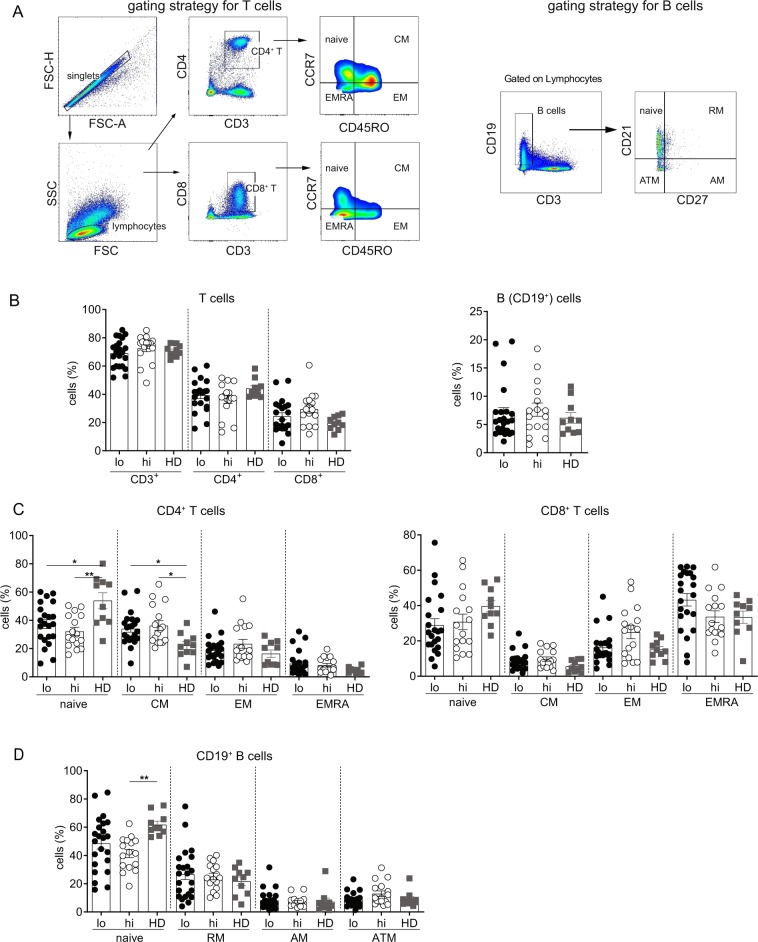
Figure 1.
Frequencies of different immune cell subsets among the HBslo (<500 IU/ml, designated as lo), HBshi (>50,000 IU/ml, designated as hi) and healthy donors (HD). (A) Gating strategies for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells and their subsets based on CD45RO and CCR7 expression; naïve (CD45RO−CCR7+), central memory (CM; CD45RO+CCR7+), effector memory (EM; CD45RO+CCR7−) and terminally differentiated effector memory (EMRA; CD45RO−CCR7−). Gating strategies for B cells and their subsets based on CD21 and CD27 expression; naïve (CD27−CD21+), resting memory (RM; CD27+CD21+), active memory (AM; CD27+CD21−) and atypical memory (ATM; CD27−CD21−). (B) Frequencies of total CD4+, CD8+ T cells and total B cells among groups. (C) Proportions of the naïve, CM, EM and EMRA subsets of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. (D) Proportions of the naïve, RM, AM and ATM subsets of B cells. Each data point represents an individual sample and horizontal line represents the median value. One-way-ANOVA/Kruskal-Wallis with Bonferroni/Dunn’s post-hoc tests for multiple comparison were performed for parametric or non-parametric data respectively. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005.