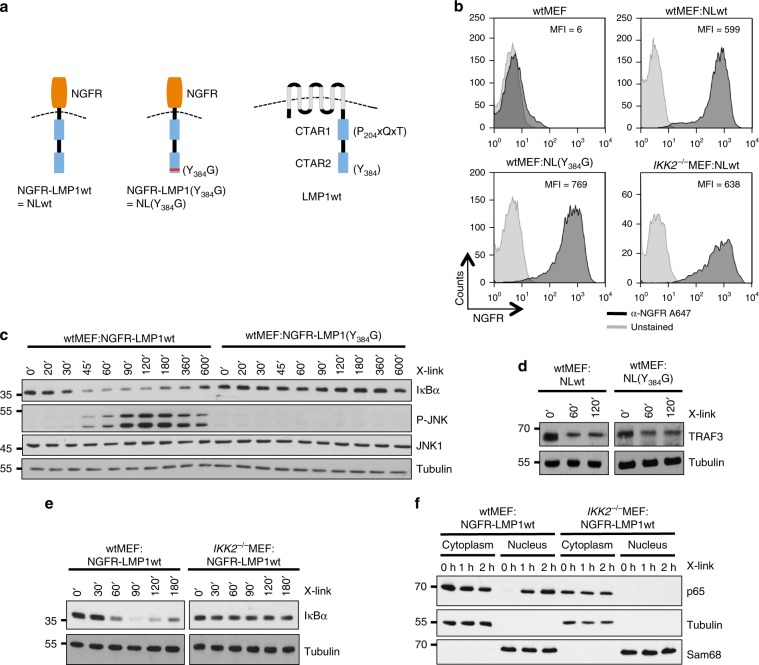
Fig. 1. Analysis of time-resolved signal transduction events induced by the CTAR2 domain of LMP1 through IKK2.
a Schematic representation of the NGFR-LMP1 (NL) fusion constructs used in this study, compared to wildtype LMP1 (right). Y384G mutation results in a dysfunctional CTAR2 domain. Activity of NGFR-LMP1 can be triggered by NGFR-directed antibody crosslinking. b Wildtype and IKK2-deficient mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) were retrovirally transduced with NGFR-LMP1 or, in the case of wildtype MEFs, also with NGFR-LMP1(Y384G). Equivalent surface expression of the chimeras was confirmed by flow cytometry. MFI mean fluorescent intensity. c Activation of canonical NF-κB and JNK is instantly triggered at CTAR2. NGFR-LMP1 constructs were activated with NGFR antibody and a crosslinking secondary antibody for the indicated times (X-link). IκBα levels and JNK phosphorylation were detected by immunoblotting. Apparent molecular weights are given in kDa. d CTAR1-induced TRAF3 depletion remains unaffected by CTAR2 inactivation. Immunoblot analysis of detergent-soluble TRAF3 protein levels after crosslinking. e Canonical NF-κB activation by LMP1 in MEF cells depends on IKK2. f LMP1-induced p65 NF-κB translocation into the nucleus requires IKK2. Cytoplasmic and nuclear p65 NF-κB levels were analysed after antibody crosslinking. b–f The data are representative of at least two independent experiments. c–f For immunoblot quantification and statistics see Supplementary Table 3.