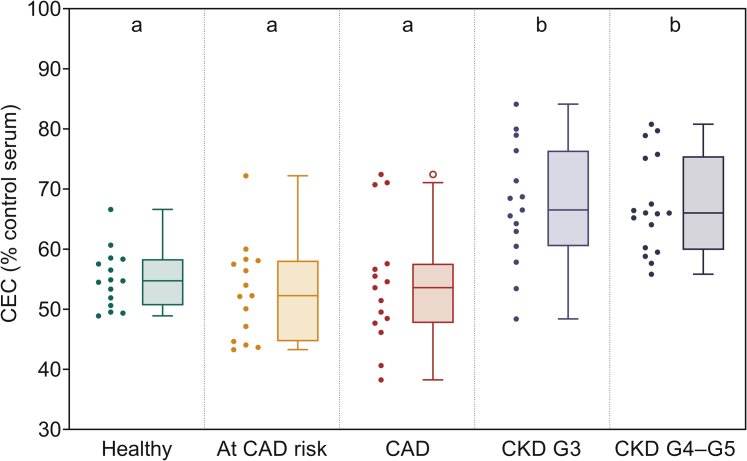
Figure 3.
Serum from patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) has significantly higher cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC) compared with healthy controls and patients with coronary artery disease (CAD). THP1 macrophages were loaded with acetylated human low-density lipoprotein (AcLDL) and radiolabeled with [3H]-cholesterol as described in the Methods section. Serum, at a final concentration of 1%, from subjects in indicated cohorts was used as the extracellular cholesterol acceptor and observed CEC was normalized to a pooled control serum sample and expressed as percentage. Data are presented as Tukey box-and-whisker plots (box divider: median; box ends: interquartile range [IQR]; whiskers: ±1.5 × IQR). Statistical analysis for overall difference between groups was performed using the Kruskal-Wallis H test (overall significance level α = 0.05), followed by the Dunn test with joint ranking (overall significance level α = 0.05 with Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons). Dissimilar letters indicate statistically significant differences.