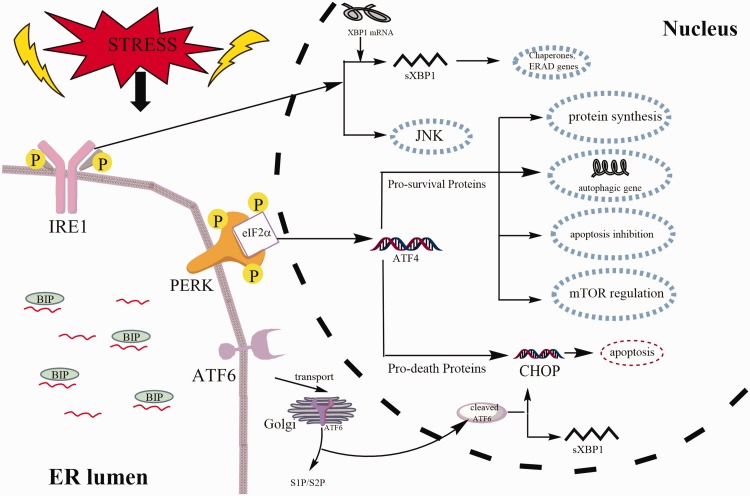
Fig. 1.
The unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway. The three types of UPR signal transducers are PERK, IRE1, and ATF6. IRE1 has both kinase and endoribonuclease identity. When IRE1 is activated, a small intron of XBP1 is removed to form sXBP1, which involves the transcription of genes that restores ER folding ability. PERK phosphorylates eIF2a attenuating mRNA translation, but it specifically induces the transcription factors ATF4 and CHOP, which will induce the occurrence of related reactions such as protein synthesis and apoptosis. ATF6 is translocated into the Golgi where it is cleaved to expose the transcriptionally active cytoplasmic domain of ATF6. The direct target of the cleaved ATF6 is the UPR proteins, such as chaperones. Also, ATF6 can also induce CHOP and XBP1 genes. PERK: protein kinase RNA-like ER kinase; IRE1: inositolrequiring enzyme 1; ATF6: activating transcription factor 6; BIP: Immunoglobulin binding protein; eIF2a: eukaryotic initiation factor 2a; XBP1: X-box binding protein; S1P: protease site 1 protease; S2P: protease site 2 protease; CHOP: transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase.