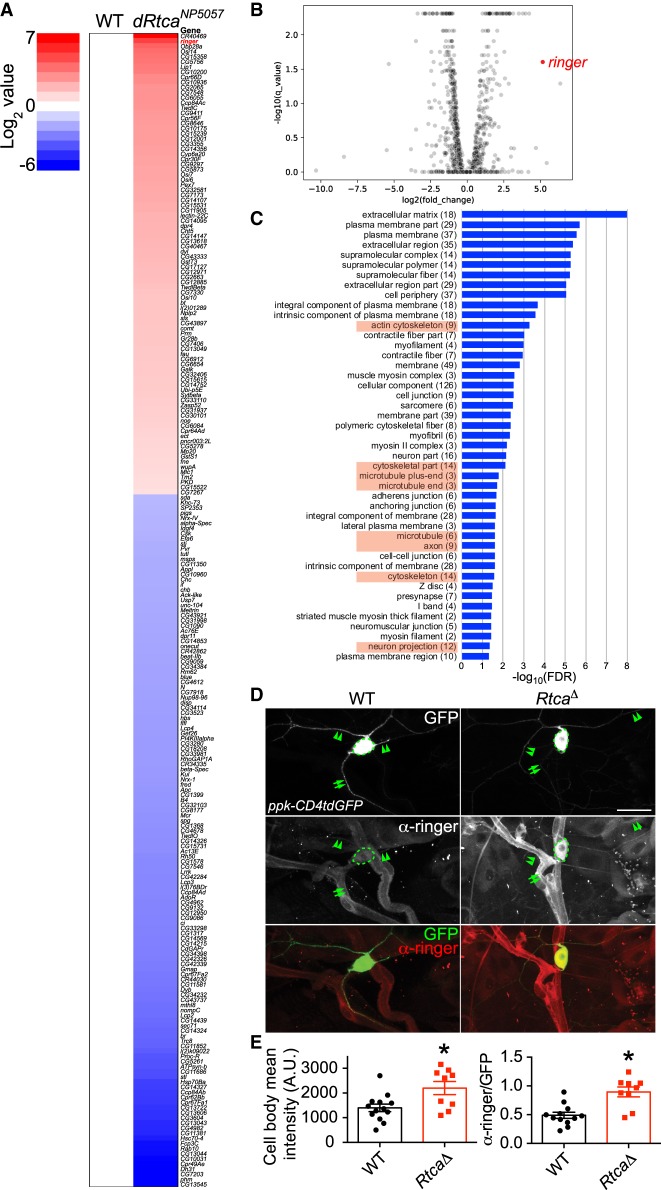
Figure 1.
Transcriptome profiling and increased ringer expression in Rtca mutants. (A) Heat map showing the significantly up-regulated (red) or down-regulated (blue) genes in a hypomorphic allele of Rtca: RtcaNP5057. Ringer, highlighted in red, is the second most up-regulated protein-coding gene. n = 3 replicates for each genotype. (B) Volcano plot showing differential gene expression in C4da neurons in RtcaNP505 versus WT. Positive log2(fold change) indicates an increase in mutants relative to WT. ringer is highlighted in red. (C) The GO term analyses (http://geneontology.org) of the differentially regulated gene sets. The pathways in the GO Cellular Component are ranked based on the false discovery rate (FDR). (D) Immunostaining for the ringer protein in larvae shows that it is expressed in various cell types including neurons, glial cells, and epithelial cells. Ringer is present in the soma (dashed circle), axon (arrows), and dendrites (arrowheads) of C4da neurons (labeled with ppk-CD4tdGFP). Ringer protein is up-regulated in a deletion allele of Rtca: RtcaΔ. (E) Ringer expression level in the soma is quantified by measuring the mean fluorescence intensity with and without normalization to GFP, and it is significantly increased in RtcaΔ. n = 9 to 13 neurons from three to five larvae. (*) P < 0.05 by two-tailed unpaired Mann-Whitney test. Scale bar, 20 μm.