Figure 3.
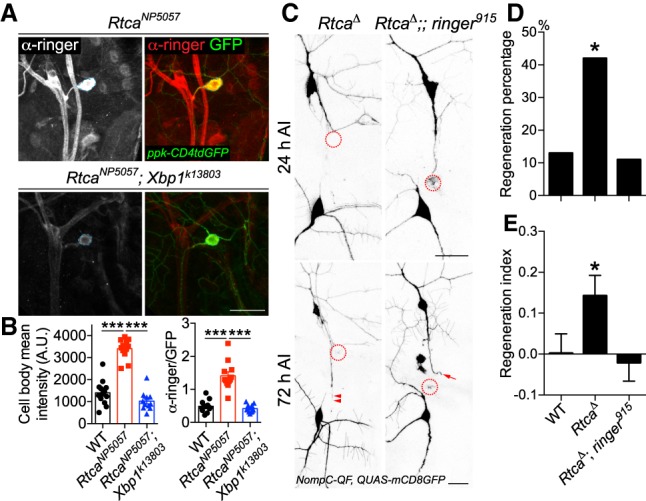
Ringer functions downstream from Rtca, in a Xbp1-dependent manner. (A) Xbp1 mediates the increase of ringer expression in Rtca mutants. The drastic increase of ringer expression in RtcaNP5057 mutants is abolished in Rtca and Xbp1 double mutants. Dashed circle marks the C4da neuron cell body. (B) The ringer immunolabeling is quantified by measuring the mean fluorescence intensity in the C4da neuron soma with and without normalization to GFP, showing that the increased ringer expression in Rtca mutants is eliminated after Xbp1 deficiency. n = 11 to 13 neurons from three to five larvae. (C) While Rtca LOF improves C3da neuron axon regeneration after peripheral injury, the enhancement is completely eliminated in Rtca and ringer double mutants. The injury site is demarcated by the dashed circle. Arrow marks axon stalling while arrowheads show the regrowing axon tips. (D,E) Quantifications of C3da neuron axon regeneration with regeneration percentage (D) and regeneration index (E). n = 19 to 24 neurons from four to six larvae. (*) P < 0.05; (***) P < 0.001 by Fisher's exact test (D), one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test (B), or Dunn's test (E). Scale bar, 20 μm.
