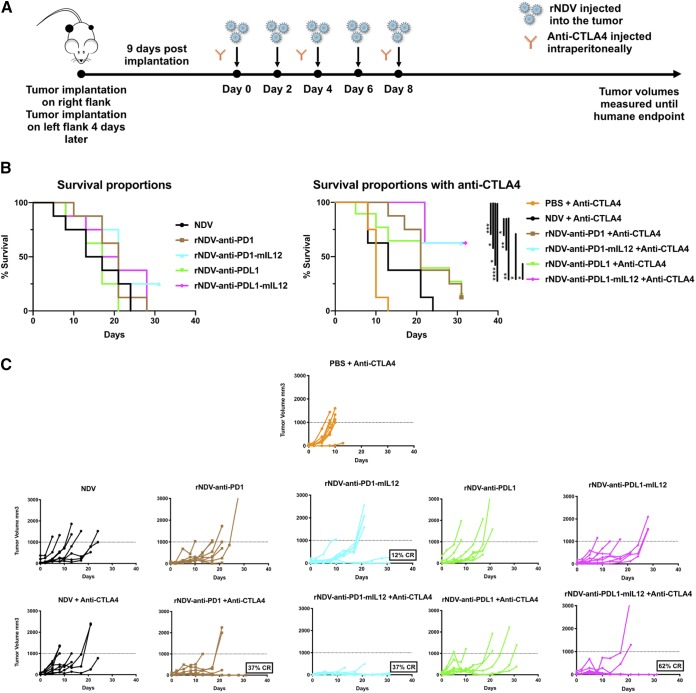
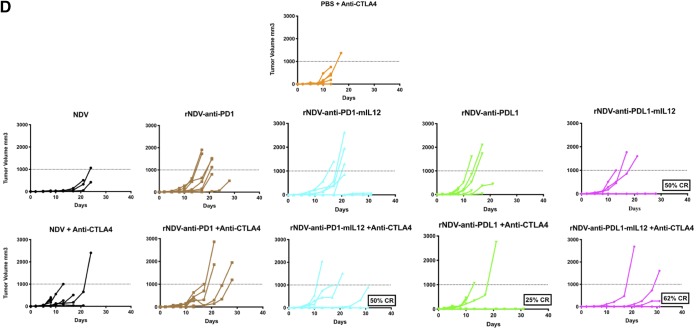
FIG 4.
rNDVs expressing checkpoint inhibitor immunocytokines intratumorally enhance tumor control and survival benefits in a bilateral-flank tumor model. (A) Mouse treatment scheme. Two hundred thousand and 100,000 B16-F10 melanoma cells were implanted in the right and left flanks of C57BL/6 mice 4 days apart. Nine days postimplantation, the tumors were treated with five intratumoral administrations of various rNDVs at 106 PFU every 2 days and three i.p. injections of anti-CTLA4 (100 μg) every 4 days. Tumor volumes were measured until the humane endpoint. (B) Overall survival percentages for the different treatment cohorts. (C and D) Individual tumor volume progressions for the treated tumor side (C) and the nontreated side (D), along with the CR percentages, for the rNDV–anti-PD1/PDL1 and rNDV–anti-PD1/PDL1–mIL-12 treatment cohorts. The data for survival were analyzed by log rank (Mantel-Cox) tests. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.