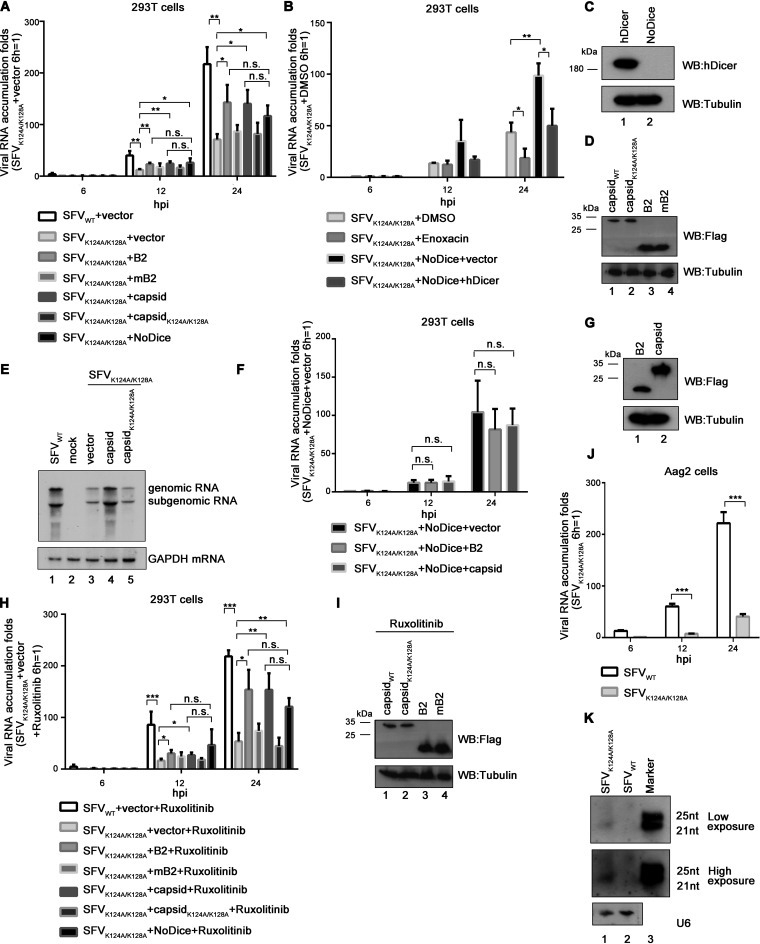
FIG 7.
The deficiency of RNAi rescued the defective replication of VSR-deficient SFV. (A) 293T or 293T-NoDice cells were transfected with either empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding NoV B2, mB2 (B2R59Q), SFV capsid, or capsidK124A/K128A as indicated. At 24 hpt, the cells were infected with SFVWT or SFVK124A/K128A at an MOI of 1. At 6, 12, and 24 hpi, the levels of SFV genomic RNAs in cells were determined by qRT-PCR, and the level of SFVK124A/K128A RNA in 293T cells at 6 hpi was defined as 1. All data represent the means and standard deviations of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (as measured by two-way ANOVA; GraphPad Prism). (B) 293T or NoDice 293T cells were transfected with either empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding human Dicer (hDicer) as indicated. At 24 hpt, the cells were treated with enoxacin (100 μM) for 1 h and then infected with SFVWT at an MOI of 1. At 6, 12, and 24 hpi, the levels of SFV genomic RNAs in cells were determined by qRT-PCR, and the level of SFVK124A/K128A RNA in 293T cells treated with DMSO at 6 hpi was defined as 1. All data represent the means and standard deviations of three independent experiments. (C and D) The expression of capsid, capsidK124A/K128A, NoV B2, mB2, or hDicer proteins in 293T or 293T-NoDice cells was detected by Western blotting. (E) 293T cells were transfected with SFV capsid or capsidK124A/K128A as indicated and then infected with SFVWT or SFVK124A/K128A at an MOI of 1. At 24 hpi, the total RNAs were extracted, the levels of SFV genomic and subgenomic RNAs were examined via Northern blotting with DIG-labeled RNA probe targeting nt 723 to 1314 of the SFV E2 coding region. GAPDH mRNA was used the loading control. (F) 293T-NoDice cells were transfected with either empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding NoV B2, SFV capsid as indicated. At 24 hpt, the cells were infected with SFVK124A/K128A at an MOI of 1. At 6, 12, and 24 hpi, the levels of SFV genomic RNAs in cells were determined by qRT-PCR, and the level of SFVK124A/K128A RNA in 293T cells transfected with either empty plasmid at 6 hpi was defined as 1. (G) The expression of SFV capsid, and NoV B2 in 293T-NoDice cells was detected by Western blotting. (H) 293T or 293T-NoDice cells were transfected with either empty plasmid or a plasmid encoding NoV B2, mB2 (B2R59Q), SFV capsid, or capsidK124A/K128A as indicated. At 24 hpt, the cells were treated with ruxolitinib (10 μM) for 1 h and then infected with SFVWT or SFVK124A/K128A at an MOI of 1. At 6, 12, and 24 hpi, the levels of SFV genomic RNAs in cells were determined by qRT-PCR, and the level of SFVK124A/K128A RNA in 293T cells at 6 hpi was defined as 1. (I) The expression of capsid, capsidK124A/K128A, NoV B2, or mB2 in ruxolitinib-treated 293T cells was detected by Western blotting. (J) Aag2 cells were infected with SFVWT or SFVK124A/K128A at an MOI of 1. At 6, 12, and 24 hpi, the levels of SFV genomic RNAs in cells were determined by qRT-PCR, and the level of SFVK124A/K128A RNA in MLF cells at 6 hpi was defined as 1. (K) Aag2 cells were infected with SFVWT or SFVK124A/K128A at an MOI of 10. At 24 hpi, the total RNAs were extracted, and the levels of vsiRNAs were examined via Northern blotting with a DIG-labeled RNA probe targeting nt 1 to 50 of antigenomic SFV RNA. U6 was used a loading control.