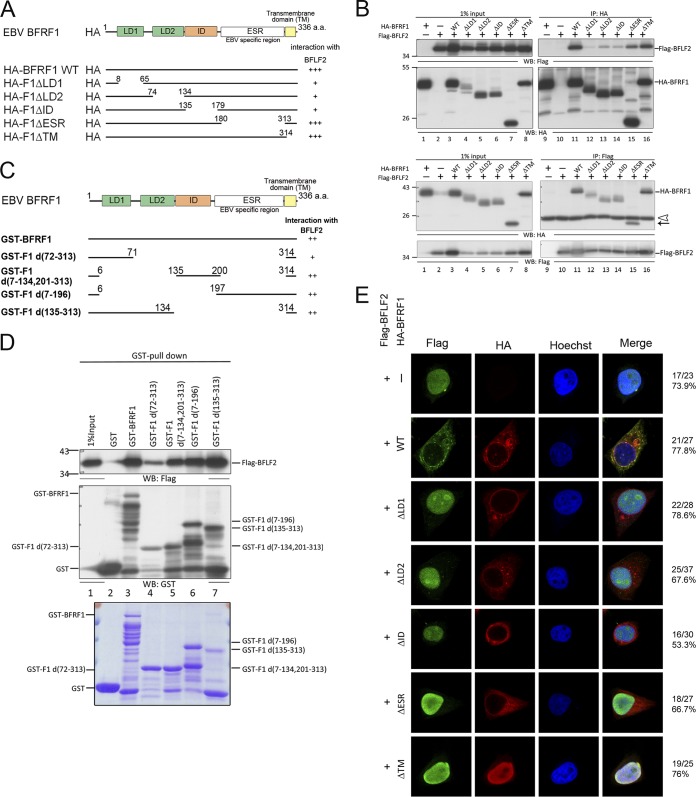
FIG 7.
Multiple domains of BFRF1 interact with BFLF2. (A) Schematic representation of predicted functional domains of BFRF1 and serial deletion mutants of HA-BFRF1. The abilities to interact with BFLF2 as detected by coimmunoprecipitation are summarized on the right. (B) Flag-BFLF2-expressing plasmid was transfected with plasmid expressing wild-type or serial deletion HA-BFRF1 mutants into HeLa cells. At 24 hpt, the lysates were harvested and immunoprecipitated with antibody against HA (top) or Flag (bottom). The immunocomplexes were then resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against HA or Flag. Two independent experiments were performed, and representative data are shown. The position of HA-F1ΔESR is indicated by an arrow. The IgG L chain is indicated by an open triangle. (C) Schematic representation of full-length and truncated GST-BFRF1 constructs. (D) Plasmid expressing Flag-BFLF2 was transfected into HeLa cells. At 24 hpt, the lysates were harvested and incubated with GST-tagged BFRF1 fusion proteins to pull down BFLF2. The interacting complexes were then resolved by 10% SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with antibodies against Flag or GST (top). The input GST-BFRF1 full-length and truncated mutants were harvested from isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG)-induced BL21 were displayed by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue (bottom). The experiment was performed two times, and representative data are shown. (E) The same plasmids as for panel B were transfected into slide-cultured HeLa cells. At 24 hpt, the slides were fixed and stained with antibodies against Flag (green) and HA (red) and then stained with Hoechst to indicate cellular DNA (blue). The slides were analyzed by confocal microscopy. The experiment was performed twice, and the numbers of cells showing the representative pattern of each group of cells are indicated from one independent experiment.