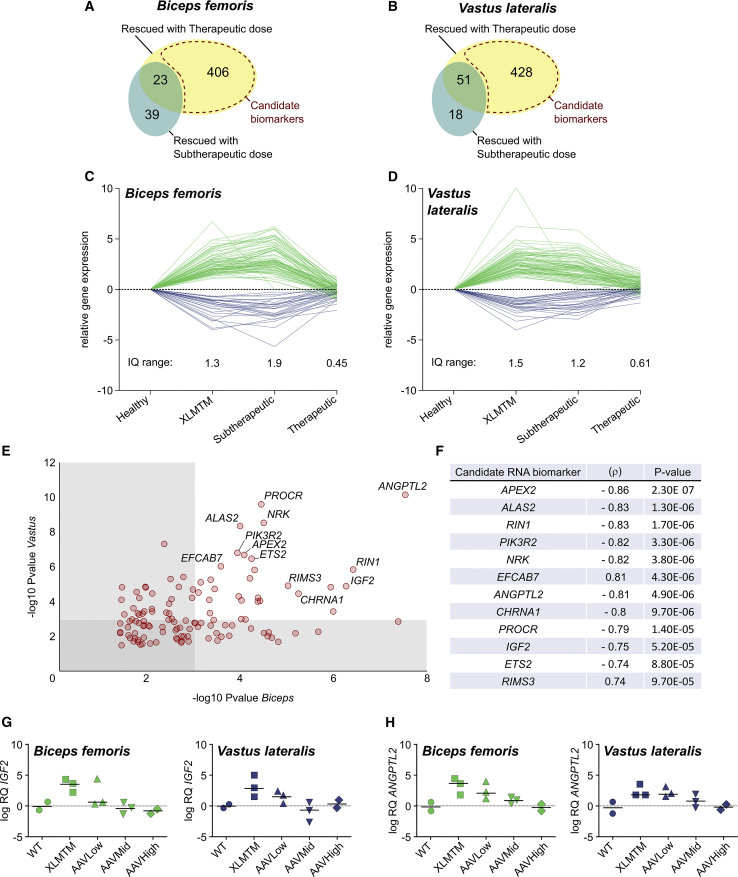
Figure 4.
Candidate RNA Biomarkers of AAV Therapeutic Effect in XLMTM Dogs
(A and B) Venn diagrams showing the number of genes with a Rescued profile and their overlap between the Sub-therapeutic and the Therapeutic groups. The Candidate Biomarker gene subsets are delineated with a dashed red area, respectively in the Biceps (A) and the Vastus (B). (C) Relative expression of the candidate biomarkers in the Biceps (C) and the Vastus (D), expressed in log FC after normalization with healthy controls. The interquartile ranges were determined from positive log FC values (negative log FC were converted into absolute values). (E) Two-dimensional dot-plot of the 120 candidate biomarkers common to the Biceps and Vastus muscles, representing the significance of the differential expression between XLMTM dogs and healthy controls (p values). Each dot represents one gene. (F) Selection of twelve RNA biomarkers of gene therapy efficacy in XLMTM dogs, ranked according to their correlation coefficient (ρ) when compared to MTM1 mRNA tag counts. The significance of this correlation is indicated (p-value). (G and H) IGF2 (G) and ANGPTL2 (H) expression levels in both muscles assessed by qRT-PCR normalized with the housekeeping gene RPL32 and represented relative to WT dogs; RQ, relative quantity = 2−ΔΔCt; log, base 2 logarithm.