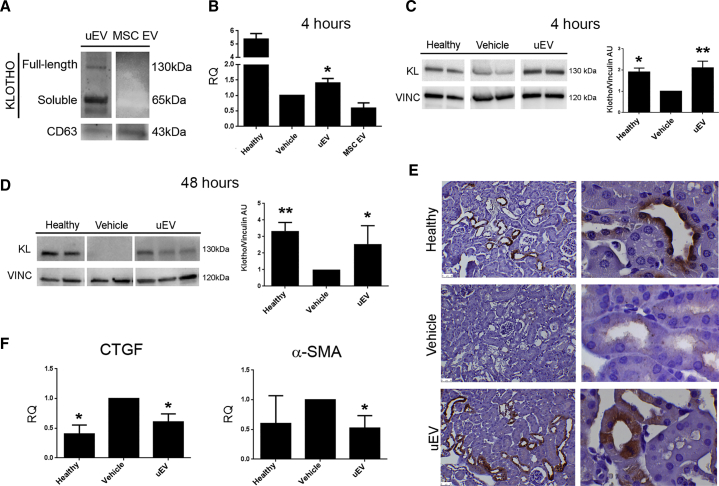
Figure 5.
uEVs Restore Klotho Levels upon AKI
(A) Representative western blot showing the presence of Klotho in uEVs, but not in MSC EVs. CD63 was used as a control exosomal marker. (B) Histogram showing the renal mRNA expression of Klotho represented by relative quantification (RQ) in healthy and AKI mice, treated with saline (vehicle), uEVs, and MSC EVs, and analyzed 4 h post EV administration. Data are normalized to GAPDH and to 1 for vehicle, and are expressed as the mean ± SEM of healthy, vehicle, and EVs (n = 3/group). Student’s t test was performed: *p < 0.05 versus vehicle. (C and D) Representative western blot of Klotho expression in kidney tissue from healthy and AKI mice, upon saline (vehicle) and uEV treatment, at days 1 (C) and 3 (D) after damage (4 and 48 h after EV injection, respectively). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of the band intensity of n = 5 (healthy group) and n = 7 (vehicle and uEV groups), normalized to vinculin and to vehicle. One-way ANOVA was performed: *p < 0.05 versus vehicle. (E) Representative micrographs showing Klotho expression in kidney tissues of healthy and AKI mice injected with saline (vehicle) and uEVs, at day 3 after damage. Original magnification ×200 and ×1,000. (F) Histograms showing the mRNA levels of CTGF and α-SMA, represented by relative quantification (RQ) in healthy and AKI mice, treated with saline (vehicle) and uEVs. Data are normalized to GAPDH and to 1 for vehicle, and are expressed as the mean ± SEM of healthy (n = 3), vehicle, and EVs (n = 7/group). One-way ANOVA was performed: *p < 0.05 versus vehicle.