Figure 3.
PKM2 Tetramerization Limits HIF1-α, Myc, and mTORC1 Signaling and Engagement of Glycolysis in CD4+ T Cells
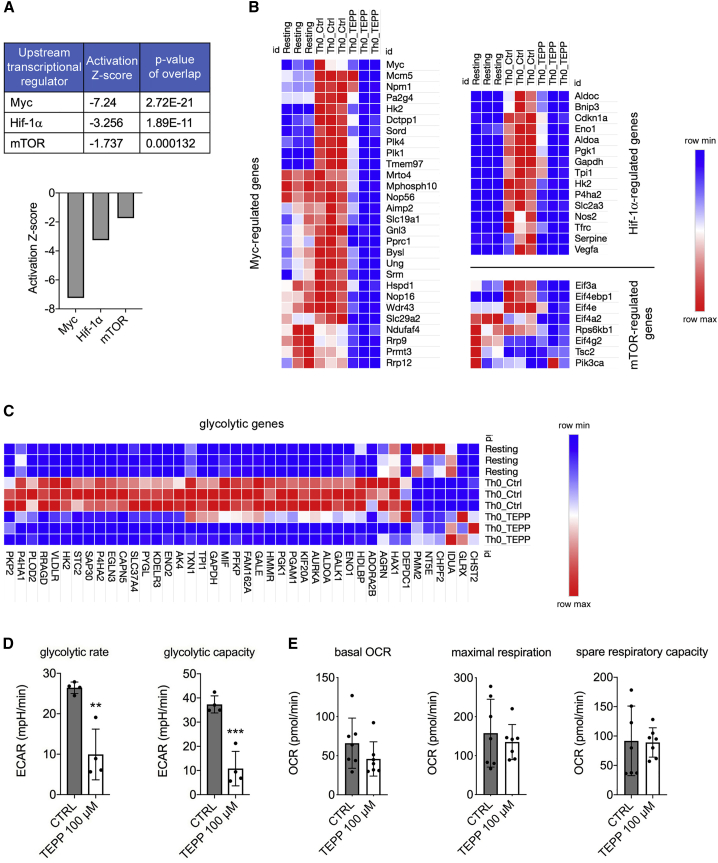
Murine CD4+ T cells were collected after 72 h of in vitro activation with CD3/CD28 antibodies in the presence of DMSO (CTRL condition) or TEPP-46 100 μM.
(A) Results of unbiased Ingenuity Pathway Analysis predicting downregulation of Myc-, Hif-1-α-, and mTOR-regulated pathways by TEPP-46.
(B) Heatmaps showing expression of Myc-, Hif-1-α-, and mTOR-regulated genes in resting T cells and T cells activated in the presence of DMSO (Th0 Ctrl) or TEPP-46 (Th0 TEPP).
(C) Heatmap showing expression of glycolytic genes in resting, Th0 Ctrl, and Th0 TEPP-46 cells.
(D and E) Cells were tested for their glycolytic capacity and oxygen consumption rate (OCR) on a Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer.
(D) Quantitative analysis of glycolytic rate and glycolytic capacity of CTRL and TEPP-46-treated cells (n = 4 from 2 independent experiments).
(E) Quantitative analysis of basal OCR, maximum respiration and spare respiratory capacity of CTRL and TEPP-46-treated cells (n = 7 from three independent experiments). For (D) and (E), data are the mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01 or ∗∗∗p < 0.001, compared to CTRL condition, by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test.