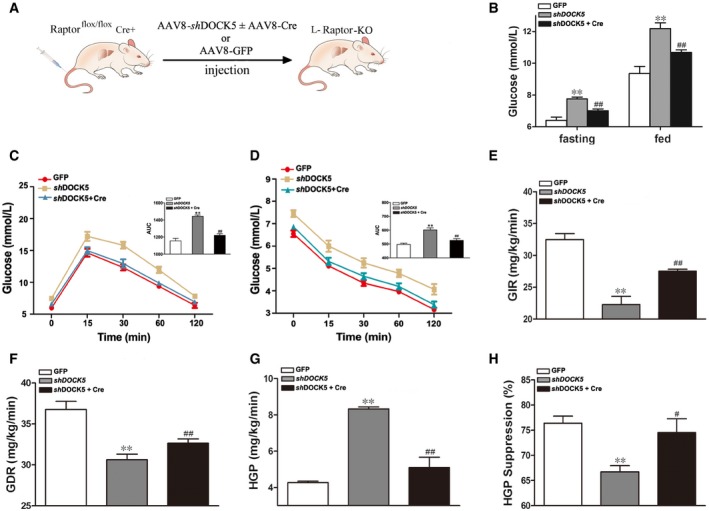
Eight‐week‐old male Raptor
flox/flox mice (Raptor
flox/flox Cre
+) were fed a HFD for 12 weeks and injected with AAV8‐
shDOCK5 ± AAV8‐Cre or AAV8‐GFP (at a dose of 3 × 10
11 vg/200 μl/mouse) via the tail vein 14 days prior to the
in vivo study.
Schematic representation of the strategy used to produce liver‐specific Raptor knockout (L‐Raptor KO) mice.
Fasting and fed blood glucose 14 days post‐infection.
Blood glucose levels and AUC during glucose tolerance tests.
Blood glucose levels and AUC during insulin tolerance tests.
Glucose infusion rate (GIR).
Glucose disposal rate (GDR).
Hepatic glucose production (HGP).
Percentage of suppression of hepatic glucose production (HGP).
Data information: AUC, the area under the curve for glucose. Data are means ± SEM (
n = 5–6 mice for each group).
P‐values were determined with
t‐test, **
P <
0.01 versus GFP group;
#
P <
0.05,
##
P <
0.01 versus
shDOCK5 group.