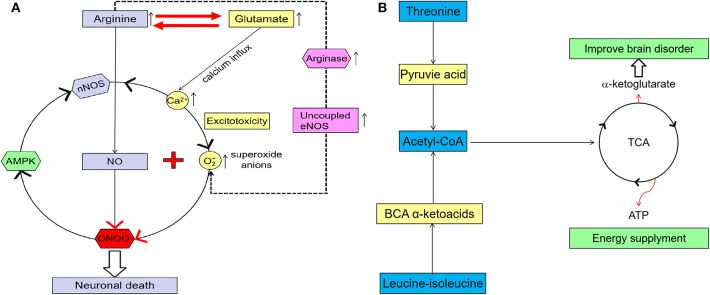
Figure 7.
(A) A higher glutamate concentration in the brain can induce excitotoxicity, and the increase of Ca2+ concentrations in the cell, which may cause mitochondrial dysfunction and increase oxidative stress and neuron death. A high arginine concentration can increase arginase activity, which leads to an uncoupling of eNOS and induces more neurotoxic substance (imaginary line). Excessive glutamate has excitotoxicity, and arginine can also increase oxidative stress and induce more neurotoxins by itself. Arginine and glutamate can be converted into each other and linked in their metabolism. When higher concentrations of arginine and glutamate come together, more neurotoxins such as peroxynitrite are produced. Adenosine monophosphate activated protein kinase (AMPK) also can be activated by peroxynitrite, so nNOS, peroxynitrite, and AMPK become one vicious cycle. All these will ultimately lead to neuronal death and functional impairment. (B) Both leucine-isoleucine and threonine can be converted to acetyl-coA and come into the TCA). TCA can provide ATP and AKG for the brain, which have an important effect on brain function recovery after stroke.