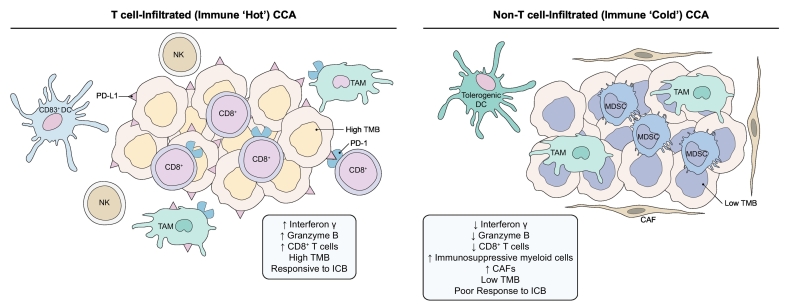
Fig. 1.
The evolving tumour immune microenvironment of CCA.
T cell-infiltrated or immune ‘hot’ CCAs have increased CD8+ T cell infiltration with enhanced interferon γ and granzyme B activity, antitumour DCs and NK cells, increased immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1 and its ligand PD-L1, and enhanced responsiveness to ICB. Non-T cell-infiltrated or immune ‘cold’ CCAs are devoid of CD8+ T cells and have a preponderance of immunosuppressive cells such as M2-like TAMs, MDSCs, and tolerogenic DCs. These tumours are generally poorly responsive to ICB. CAF, cancer-associated fibroblast; CCA, cholangiocarcinoma; DC, dendritic cell; ICB, immune checkpoint blockade; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; NK, natural killer; PD-1, programmed death-1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; TAM, tumour-associated macrophage; TMB, tumour mutational burden.