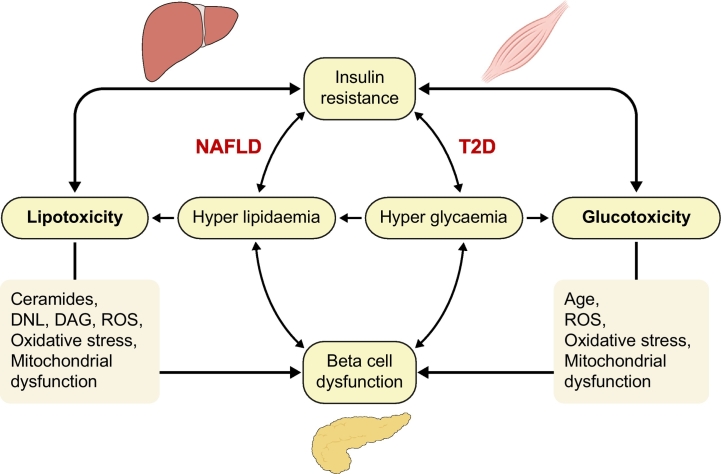
Fig. 4.
Relationship between lipo- and glucotoxicity, insulin resistance and beta-cell function.
Both lipotoxicity and glucotoxicity contribute to insulin resistance, ectopic fat accumulation and beta-cell dysfunction and vice versa. In NAFLD, lipotoxicity and insulin resistance have been recognised as pathophysiological mechanisms responsible of development and progression to a more severe form of this disease. T2D is a chronic condition of glucotoxicity, although also lipotoxicity is often present and are responsible not only of insulin resistance but also of impaired insulin secretion. DAG, diacylglycerol; DNL, de novo lipogenesis; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; ROS, reactive oxygen species; T2D, type 2 diabetes.